The Coffee Portal
Coffee | Drinks | Coffeehouses | Companies | Culture | Preparation | Production
Introduction

Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It has the highest sales in the world market for hot drinks.
The seeds of the Coffea plant's fruits are separated to produce unroasted green coffee beans. The beans are roasted and then ground into fine particles typically steeped in hot water before being filtered out, producing a cup of coffee. It is usually served hot, although chilled or iced coffee is common. Coffee can be prepared and presented in a variety of ways (e.g., espresso, French press, caffè latte, or already-brewed canned coffee). Sugar, sugar substitutes, milk, and cream are often added to mask the bitter taste or enhance the flavor.
Though coffee is now a global commodity, it has a long history tied closely to food traditions around the Red Sea. The earliest credible evidence of coffee drinking as the modern beverage appears in modern-day Yemen in southern Arabia in the middle of the 15th century in Sufi shrines, where coffee seeds were first roasted and brewed in a manner similar to how it is now prepared for drinking. The coffee beans were procured by the Yemenis from the Ethiopian Highlands via coastal Somali intermediaries, and cultivated in Yemen. By the 16th century, the drink had reached the rest of the Middle East and North Africa, later spreading to Europe. (Full article...)
Selected article -
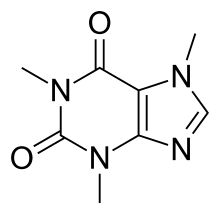
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine class. It is mainly used as a eugeroic (wakefulness promoter) or as a mild cognitive enhancer to increase alertness and attentional performance. Caffeine acts by blocking binding of adenosine to the adenosine A1 receptor, which enhances release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Caffeine has a three-dimensional structure similar to that of adenosine, which allows it to bind and block its receptors. Caffeine also increases cyclic AMP levels through nonselective inhibition of phosphodiesterase.
Caffeine is a bitter, white crystalline purine, a methylxanthine alkaloid, and is chemically related to the adenine and guanine bases of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). It is found in the seeds, fruits, nuts, or leaves of a number of plants native to Africa, East Asia and South America and helps to protect them against herbivores and from competition by preventing the germination of nearby seeds, as well as encouraging consumption by select animals such as honey bees. The best-known source of caffeine is the coffee bean, the seed of the Coffea plant. People may drink beverages containing caffeine to relieve or prevent drowsiness and to improve cognitive performance. To make these drinks, caffeine is extracted by steeping the plant product in water, a process called infusion. Caffeine-containing drinks, such as coffee, tea, and cola, are consumed globally in high volumes. In 2020, almost 10 million tonnes of coffee beans were consumed globally. Caffeine is the world's most widely consumed psychoactive drug. Unlike most other psychoactive substances, caffeine remains largely unregulated and legal in nearly all parts of the world. Caffeine is also an outlier as its use is seen as socially acceptable in most cultures and even encouraged in others.
General images -
More did you know? -
Selected drink -

Ginseng coffee is a beverage prepared from coffee and ginseng root.
In Indonesia, the company Citra Nusa Insan Cemerlang (CNI) began marketing ginseng coffee in 1994. By the early 2010s, ginseng coffee products had been marketed in China, India, Japan, Malaysia, the Philippines, and South Korea. At that time the typical production process consisted of simple mixing of ginseng powder and instant coffee powder. Several authors with the Korea Food Research Institute conducted research into a new production process whereby whole coffee beans would be coated with ginseng extract following roasting and then ground and brewed. (Full article...)Selected image -

Did you know (auto-generated)

- ... that the Claudia Quintet was born out of an incident at alt.coffee?
- ... that Monmouth Coffee Company in Covent Garden was one of the foundations for the third wave of coffee in London?
- ... that during the October 1980 West Nile campaign, rebels were initially hailed as "liberators", only for them to start looting coffee?
- ... that Coffee Talk Episode 2: Hibiscus & Butterfly was released after the main creator of Coffee Talk died in March 2022?
- ... that the city council of Bandung in the Dutch East Indies initially met at the site of a former coffee-packing factory?
- ... that in a copyright infringement case over a coffee-table history of the Grateful Dead, the Second Circuit held that a reuser can still claim fair use despite negotiating with the rights holder?
- ... that Justly Watson died suddenly in 1757 from the effects of poison administered in his coffee, it was believed, by a servant?
- ... that the short story collection Drinking Coffee Elsewhere was chosen by John Updike as a selection for the Today Show book club on NBC?
Topics
Categories
Related portals
Related WikiProjects
- WikiProject Agriculture
- WikiProject Beer
- WikiProject Food and Drink
- WikiProject Spirits (semi-active)
- Wikiproject Wine (semi-active)
- WikiProject Bartending (Inactive)
- WikiProject Breakfast (inactive)
- Wikiproject Bacon (inactive)
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Web resources

- World Coffee Research – a 501 (c)(5) nonprofit program of the international coffee industry. (Wikipedia article: World Coffee Research)
- Coffee Research Foundation – based in Kenya, and founded in 1908
- Central Coffee Research Institute – based in Chickmagalur District, India, and founded in 1915
Wikipedia's portals
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search




















































































