Back بوابة:مطاعم وطعام Arabic প্রবেশদ্বার:খাদ্য Bengali/Bangla دەروازە:خۆراک CKB Portál:Gastronomie Czech Portal:Essen und Trinken German Portalo:Nutrado kaj gastronomio Esperanto Portal:Alimentos Spanish Portaal:Toit Estonian درگاه:خوراک Persian Portail:Alimentation et gastronomie French
F o o d
A portal dedicated to food and foodways
Introduction


Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells to provide energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth. Different species of animals have different feeding behaviours that satisfy the needs of their metabolisms and have evolved to fill a specific ecological niche within specific geographical contexts.
Omnivorous humans are highly adaptable and have adapted to obtaining food in many different ecosystems. Humans generally use cooking to prepare food for consumption. The majority of the food energy required is supplied by the industrial food industry, which produces food through intensive agriculture and distributes it through complex food processing and food distribution systems. This system of conventional agriculture relies heavily on fossil fuels, which means that the food and agricultural systems are one of the major contributors to climate change, accounting for as much as 37% of total greenhouse gas emissions. (Full article...)
Cooking, also known as cookery or professionally as the culinary arts, is the art, science and craft of using heat to make food more palatable, digestible, nutritious, or safe. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from grilling food over an open fire, to using electric stoves, to baking in various types of ovens, to boiling and blanching in water, reflecting local conditions, techniques and traditions. Cooking is an aspect of all human societies and a cultural universal.
Preparing food with heat or fire is an activity unique to humans. Archeological evidence of cooking fires from at least 300,000 years ago exists, but some estimate that humans started cooking up to 2 million years ago.
The expansion of agriculture, commerce, trade, and transportation between civilizations in different regions offered cooks many new ingredients. New inventions and technologies, such as the invention of pottery for holding and boiling of water, expanded cooking techniques. Some modern cooks apply advanced scientific techniques to food preparation to further enhance the flavor of the dish served. (Full article...)
Amal Women's Training Center and Moroccan Restaurant (Arabic: جمعية الامل لفنون الطبخ; French: Association Amal pour les Arts culinaires en faveur des femmes nécessiteuses) is a non-profit organization in Marrakesh, Morocco, that helps disadvantaged women gain work experience by training them in the preparation of Moroccan food and international food. The center was established in 2012 by Nora Belahcen Fitzgerald. Each year between 30 and 40 women complete four to six months of training, which often leads to them finding employment in a relevant field. (Full article...)
Selected article –

Canned or tinned fish are food fish which have been processed, sealed in an airtight container such as a sealed tin can, and subjected to heat. Canning is a method of preserving food, and provides a typical shelf life ranging from one to five years. They are usually opened via a can opener, but sometimes have a pull-tab so that they can be opened by hand. In the past it was common for many cans to have a key that would be turned to peel the lid of the tin off; most predominately sardines, among others.
Fish have low acidity levels at which microbes can flourish. From a public safety point of view, foods with low acidity (pH greater than 4.6) need sterilization at high temperatures of 116–130 °C (241–266 °F). Achieving temperatures above the boiling point requires pressurized cooking. After sterilization, the containing can prevents microorganisms from entering and proliferating inside. Other than sterilization, no method is dependable as a preservative. For example, the microorganism Clostridium botulinum (which causes botulism) can only be eliminated at temperatures above the boiling point. (Full article...)
Selected cuisine -

The cuisine of early modern Europe (c. 1500–1800) was a mix of dishes inherited from medieval cuisine combined with innovations that would persist in the modern era.
The discovery of the New World, the establishment of new trade routes with Asia and increased foreign influences from sub-Saharan Africa and the Middle East meant that Europeans became familiarized with a multitude of new foodstuffs. Spices that previously had been prohibitively expensive luxuries, such as pepper, cinnamon, cloves, nutmeg, and ginger, soon became available to the majority population, and the introduction of new plants coming from the New World and India like maize, potato, sweet potato, chili pepper, cocoa, vanilla, tomato, coffee, and tea transformed European cuisine forever. (Full article...)
Selected ingredient –
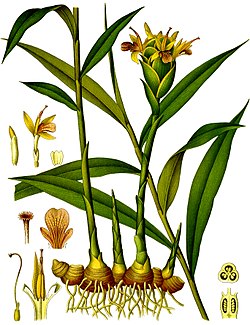
Ginger (Zingiber officinale) is a flowering plant whose rhizome, ginger root or ginger, is widely used as a spice and a folk medicine. It is an herbaceous perennial that grows annual pseudostems (false stems made of the rolled bases of leaves) about one meter tall, bearing narrow leaf blades. The inflorescences bear flowers having pale yellow petals with purple edges, and arise directly from the rhizome on separate shoots.
Ginger is in the family Zingiberaceae, which also includes turmeric (Curcuma longa), cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum), and galangal. Ginger originated in Maritime Southeast Asia and was likely domesticated first by the Austronesian peoples. It was transported with them throughout the Indo-Pacific during the Austronesian expansion (c. 5,000 BP), reaching as far as Hawaii. Ginger is one of the first spices to have been exported from Asia, arriving in Europe with the spice trade, and was used by ancient Greeks and Romans. The distantly related dicots in the genus Asarum are commonly called wild ginger because of their similar taste. (Full article...)
Selected recipe –
Bruschetta (/bruˈskɛtə, -ˈʃɛtə/ broo-SKET-ə, -SHET-ə, Italian: [bɾuˈsketta] ⓘ) is an Italian appetizer (antipasto) consisting of grilled bread topped with garlic, olive oil, and salt. Most commonly it is served with toppings of tomatoes, vegetables, beans, cured meat or cheese. In Italy, bruschetta is often prepared using a brustolina grill. (Full article...)
Borscht (English: /ˈbɔːrʃt/ ⓘ) is a sour soup, made with meat stock, vegetables and seasonings, common in Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. In English, the word borscht is most often associated with the soup's variant of Ukrainian origin, made with red beetroots as one of the main ingredients, which give the dish its distinctive red color. The same name, however, is also used for a wide selection of sour-tasting soups without beetroots, such as sorrel-based green borscht, rye-based white borscht, and cabbage borscht.
Borscht derives from an ancient soup originally cooked from pickled stems, leaves and umbels of common hogweed (Heracleum sphondylium), an herbaceous plant growing in damp meadows, which lent the dish its Slavic name. With time, it evolved into a diverse array of tart soups, among which the Ukrainian beet-based red borscht has become the most popular. It is typically made by combining meat or bone stock with sautéed vegetables, which—as well as beetroots—usually include cabbage, carrots, onions, potatoes, and tomatoes. Depending on the recipe, borscht may include meat or fish, or be purely vegetarian; it may be served either hot or cold, and it may range from a hearty one-pot meal to a clear broth or a smooth drink. It is often served with smetana or sour cream, hard-boiled eggs or potatoes, but there exists an ample choice of more involved garnishes and side dishes, such as uszka or pampushky, that can be served with the soup. (Full article...)
Selected image –

Selected biography –
B. April 1, 1755, Belley, France – d. February 2, 1826, Paris
"Tell me what you eat, and I will tell you what you are."
Jean Anthelme Brillat-Savarin (French pronunciation: [ʒɑ̃ ɑ̃tɛlm bʁija savaʁɛ̃]; 2 April 1755 – 2 February 1826) was a French lawyer and politician, who, as the author of Physiologie du goût (The Physiology of Taste), became celebrated for his culinary reminiscences and reflections on the craft and science of cookery and the art of eating.
Rising to modest eminence in the last years of France's Ancien Régime, Brillat-Savarin had to escape into exile when the Reign of Terror began in 1793. He spent nearly three years in the United States, teaching French and playing the violin to support himself, before returning to France when it became safe to do so, resuming his career as a lawyer, and rising to the top of the French judiciary. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) –

- ... that the Japanese TV show Iron Chef gained a cult following on a San Francisco TV station before it was dubbed into English and aired on the Food Network?
- ... that Gleaners Food Bank has served more than 700 million pounds (320 million kg) of food in Indiana?
- ... that not all military rations are food?
- ... that on July 11, 2022, millions of dollars worth of jewelry was stolen from the back of a truck while one driver was getting food at a California truck stop and the other one was asleep in the cab?
- ... that agronomist Simon Groot was awarded the 2019 World Food Prize for "benefiting hundreds of millions of consumers with greater access to nutritious vegetables"?
- ... that Mitch Torres is a "self-proclaimed damper destroyer"?
More did you know –
Related portals
Food topics
The following are topics relating to food
Categories
Food list articles
- See also: Lists of foods and Category:Lists of drinks
The following are some Food list articles on Wikipedia:

- American cheeses
- Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée cheeses
- Apple cultivars
- Bacon dishes
- Bacon substitutes
- Basil cultivars
- Breads
- Breakfast beverages
- Breakfast cereals
- Breakfast foods
- British cheeses
- Cakes
- Candies
- Cheeses
- Cheese soups
- Christmas dishes (list)
- Cocktails
- Cookies
- Dishes using coconut milk
- Diets
- Doughnut varieties
- Egg dishes
- Fermented soy products
- Food additives
- Food additives (Codex Alimentarius)
- Foods named after people
- French cheeses
- French dishes
- Fried dough foods
- Fruits
- List of hamburgers
- Herbs and spices
- Hors d'oeuvre
- Indian dishes
- Indian snack foods
- Indonesian dishes
- Italian dishes
- Japanese snacks
- Japanese dishes
- Jewish dishes
- Kebabs
- Korean beverages
- Mango cultivars
- Moroccan dishes
- Pasta
- Pastries
- Philippine snack food
- Pies, tarts and flans
- Poppy seed pastries and dishes
- Potato dishes
- Puddings
- Raw fish dishes
- Rice dishes
- Rolled foods
- Sauces
- Seafood
- Seeds
- Sandwiches
- Snack foods
- Soft drinks by country
- Soul foods and dishes
- Soups
- Stews
- Street foods
- Tapas
- Turkish dishes
- Twice-baked foods
- Vegetable oils
- Vegetables
- Vodkas
Things you can do
Related WikiProjects
| Parent project: WikiProject Food and Drink | |
| Child projects: | Task forces: (All inactive) |
|
|
| Related projects: | |
New articles
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2025-05-12 19:15 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- Misfits Bar and Lounge (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Another Believer (talk · contribs · new pages (139)) started on 2025-05-12, score: 10
- Major League Chew (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 194.125.116.90 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-12, score: 10
- Kevin Bazner (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RandomMe98 (talk · contribs · new pages (32)) started on 2025-05-12, score: 10
- Health benefits of quitting alcohol (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Itemirus (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-12, score: 10
- The Black Market, Cork (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CeltBrowne (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2025-05-11, score: 10
- Fabio Baldé (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ortizesp (talk · contribs · new pages (43)) started on 2025-05-11, score: 10
- Faraa (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jhilmilkasture (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 10
- Cranberry scare of 1959 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BrokenSegue (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-11, score: 10
- Horats panir (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barseghian Lilia (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2025-05-11, score: 20
- Imo Shochu (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Velikov817 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2025-05-11, score: 10
- Gane (Kyushu food) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Velikov817 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2025-05-11, score: 10
- International Flavor (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 31.216.237.178 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-10, score: 10
- Round Rock Donuts (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TerraFrost (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-10, score: 10
- Fukure-Gashi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Velikov817 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2025-05-10, score: 20
- Ballard Brewery District (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by White 720 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-05-10, score: 10
- Shima tofu (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Velikov817 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2025-05-09, score: 10
- Hot butter cuttlefish (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by NandaAbeysekera (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-09, score: 10
- Lee Jang-woo (politician) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by LandAndTree (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-05-09, score: 10
- 2025–26 West Ham United F.C. season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Skyblueshaun (talk · contribs · new pages (56)) started on 2025-05-09, score: 10
- Bishnupur Motichoor Laddu (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MaheshPatil95 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-05-09, score: 30
- Giuliano Bugialli (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ketil3 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-05-09, score: 10
- Ikinari Dango (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Velikov817 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2025-05-09, score: 30
- Maithil Brahmin Bhoj (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sntshkumar750 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2025-05-08, score: 20
- Just Desserts (Chew) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 185.57.103.155 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-08, score: 10
- California Burrito (India) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fanueldude (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-08, score: 10
- Odette Mascarenhas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SerChevalerie (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-07, score: 10
- Rose City Food Park (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Another Believer (talk · contribs · new pages (139)) started on 2025-05-07, score: 10
- Take Your Pick of Disgusting Foods (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Astaire (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 20
- Tucci in Italy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wikipedical (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 10
- Ruby Jewel (company) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Another Believer (talk · contribs · new pages (139)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 10
- Prime Seafood Palace (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Another Believer (talk · contribs · new pages (139)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 10
- Cultured Caveman (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Another Believer (talk · contribs · new pages (139)) started on 2025-05-05, score: 10
- QED Coffee (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Another Believer (talk · contribs · new pages (139)) started on 2025-05-05, score: 10
- Computer Graphic (advertisement) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TangoTizerWolfstone (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 10
- National Agri-trade and Food Safety Authority (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mhaseeb99 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 10
- Rodd's (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Georgeykiwi (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 10
- Good Food Nation (Scotland) Act 2022 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Landpin (talk · contribs · new pages (110)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 10
- Digital Outdoor Menu Board (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Floating Orb (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-05-03, score: 10
- Breadfast (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Therecipeguy (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-04-28, score: 20
- Chanakh (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barseghian Lilia (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2025-05-03, score: 10
- Banfi Vintners (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dresq23 (talk · contribs · new pages (26)) started on 2025-05-03, score: 10
- Wheein (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 124.104.16.92 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2025-05-03, score: 10
- Tipsy Scoop (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Another Believer (talk · contribs · new pages (139)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 10
- Old Phone (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Max24 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 10
- Harriet Hayes Skinner (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Throughthemind (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 10
- Stir-fried glutinous rice (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Uuueol (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 10
- International Villager (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shink77 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-01, score: 10
- Club Ripples (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Eric Carpenter (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-01, score: 10
- Bacha Coffee (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by V3MBBa (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-05-01, score: 30
- Mogu Mogu (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Paul 012 (talk · contribs · new pages (35)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 20
- Kolae (cooking) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Terabyte646 (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 10
- St. Dalfour France (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Riddler10 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-04-29, score: 30
- Juweri gurtik (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Maor X (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 30
- Kyushu soy sauce (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Velikov817 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 10
- Kolae (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Terabyte646 (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 10
- All Asimov and No Fresh Air (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mattl (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-29, score: 10
- Rey Amargo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Another Believer (talk · contribs · new pages (139)) started on 2025-04-29, score: 10
- All Asimov And No Fresh Air (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mattl (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-29, score: 10
- Mohamadou Kanté (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Paul Vaurie (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2025-04-28, score: 10
- Ami-meshi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Velikov817 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2025-04-28, score: 10
- A Thousand Clowns (play) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HesioneHushabye (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-28, score: 10
- 2025 Andy's Frozen Custard 300 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Brycenrichter (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2025-04-28, score: 10
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Sources
More portals
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search