Back بوابة:طاقة متجددة Arabic Portail:Énergie renouvelable French Portal:Tenaga boleh diperbaharui Malay Portal:可再生能源 Chinese
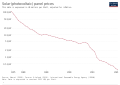
Introduction Renewable energy (or green energy) is energy from renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind power and hydropower. Bioenergy and geothermal power are also significant in some countries. Some also consider nuclear power a renewable power source, although this is controversial. Renewable energy installations can be large or small and are suited for both urban and rural areas. Renewable energy is often deployed together with further electrification. This has several benefits: electricity can move heat and vehicles efficiently, and is clean at the point of consumption. Variable renewable energy sources are those that have a fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power. In contrast, controllable renewable energy sources include dammed hydroelectricity, bioenergy, or geothermal power. Renewable energy systems have rapidly become more efficient and cheaper over the past 30 years. A large majority of worldwide newly installed electricity capacity is now renewable. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, have seen significant cost reductions over the past decade, making them more competitive with traditional fossil fuels. In most countries, photovoltaic solar or onshore wind are the cheapest new-build electricity. From 2011 to 2021, renewable energy grew from 20% to 28% of global electricity supply. Power from sun and wind accounted for most of this increase, growing from a combined 2% to 10%. Use of fossil energy shrank from 68% to 62%. In 2022, renewables accounted for 30% of global electricity generation, and are projected to reach over 42% by 2028. Many countries already have renewables contributing more than 20% of their total energy supply, with some generating over half or even all their electricity from renewable sources. The main motivation to replace fossil fuels with renewable energy sources is to slow and eventually stop climate change, which is widely agreed to be caused mostly by greenhouse gas emissions. In general, renewable energy sources cause much lower emissions than fossil fuels. The International Energy Agency estimates that to achieve net zero emissions by 2050, 90% of global electricity generation will need to be produced from renewable sources. Renewables also cause much less air pollution than fossil fuels, improving public health, and are less noisy. The deployment of renewable energy still faces obstacles, especially fossil fuel subsidies, lobbying by incumbent power providers, and local opposition to the use of land for renewables installations. Like all mining, the extraction of minerals required for many renewable energy technologies also results in environmental damage. In addition, although most renewable energy sources are sustainable, some are not. For example, some biomass sources are unsustainable at current rates of exploitation. (Full article...) Selected article - Grand Coulee Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, built to produce hydroelectric power and provide irrigation water. Constructed between 1933 and 1942, Grand Coulee originally had two powerhouses. The third powerhouse ("Nat"), completed in 1974 to increase energy production, makes Grand Coulee the largest power station in the United States by nameplate capacity at 6,809 MW. The proposal to build the dam was the focus of a bitter debate during the 1920s between two groups. One group wanted to irrigate the ancient Grand Coulee with a gravity canal while the other pursued a high dam and pumping scheme. The dam supporters won in 1933, but, although they fully intended otherwise, the initial proposal by the Bureau of Reclamation was for a "low dam" 290 feet (88 m) tall which would generate electricity without supporting irrigation. That year, the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation and a consortium of three companies called MWAK (Mason-Walsh-Atkinson Kier Company) began construction on a high dam, although they had received approval for a low dam. After visiting the construction site in August 1934, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt endorsed the "high dam" design, which at 550 ft (168 m) high would provide enough electricity to pump water into the Columbia basin for irrigation. Congress approved the high dam in 1935, and it was completed in 1942. The first waters overtopped Grand Coulee's spillway on June 1 of that year. Power from the dam fueled the growing industries of the Northwest United States during World War II. Between 1967 and 1974, the third powerplant was constructed. The decision to construct the additional facility was influenced by growing energy demand, regulated river flows stipulated in the Columbia River Treaty with Canada, and competition with the Soviet Union. Through a series of upgrades and the installation of pump-generators, the dam now supplies four power stations with an installed capacity of 6,809 MW. As the centerpiece of the Columbia Basin Project, the dam's reservoir supplies water for the irrigation of 671,000 acres (2,700 km2). (Full article...)Quotations -
– Al Gore, Our Choice, 2009, p. 58. Main topicsRenewable energy sourcesGeneralRenewable energy commercialization · Smart grid · Timeline of sustainable energy research 2020–present Renewable energy by countryList of countries by electricity production from renewable sources
WikiProjectsWikiProjects connected with renewable energy: Selected image -
The BedZED housing development in London was designed to use only energy from renewable sources generated on site. Selected biography -Jeremy Leggett is a British social entrepreneur and writer. He founded and was a board director of Solarcentury from 1997 to 2020, an international solar solutions company, and founded and was chair of SolarAid, a charity funded with 5% of Solarcentury's annual profits that helps solar-lighting entrepreneurs get started in Africa (2006–2020). SolarAid owns a retail brand SunnyMoney that was for a time Africa's top-seller of solar lighting, having sold well over a million solar lights, all profits recycled to the cause of eradicating the kerosene lantern from Africa. Leggett is winner of the first Hillary Laureate for International Leadership in Climate Change (2009), a Gothenburg Prize (2015), the first non-Dutch winner of a Royal Dutch Honorary Sustainability Award (2016), and has been described in the Observer as "Britain’s most respected green energy boss." He is the author of five books: "The Winning of The Carbon War", an account of what he sees as the "turnaround years" in the dawn of the global energy transition, 2013–2015, with an update edition spanning 2016–2017, "The Energy of Nations" (2013), "The Solar Century" (2009), "Half Gone" (2005) and "The Carbon War" (2000). He continues to write on his blog, and in occasional articles for national media. He lectured on short courses in business and society at the Universities of Cambridge (UK) and St Gallen (Switzerland). His vision is of a renaissance in civilisation aided or even triggered by renewable energy and its intrinsic social benefits. (Full article...)Did you know? -... that the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) published Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation (SRREN) in May 2011 ? The IPCC examined renewable energy and energy efficiency in its fourth assessment report, published in 2007, but members have now decided that renewable energy commercialization merits in-depth coverage because of its importance in reducing carbon emissions. General images -The following are images from various renewable energy-related articles on Wikipedia.
Related portalsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search



































![Image 33Concentrated solar panels are getting a power boost. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) will be testing a new concentrated solar power system – one that can help natural gas power plants reduce their fuel usage by up to 20 percent.[needs update] (from Solar energy)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/82/Photo_of_the_Week-_Boosting_Solar_Technology_%288722948189%29.jpg/120px-Photo_of_the_Week-_Boosting_Solar_Technology_%288722948189%29.jpg)