
Back بوابة:الأعاصير المدارية Arabic Portal:Ciclons tropicals Catalan Portal:Ciclones tropicales Spanish 포털:태풍 Korean Portaal:Tropische cyclonen Dutch Portal:Ciclones tropicais Portuguese สถานีย่อย:พายุหมุนเขตร้อน Thai Portal:熱帶氣旋 Chinese
The Tropical Cyclones Portal

A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center, a closed low-level circulation and a spiral arrangement of numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rainfall. Tropical cyclones feed on the heat released when moist air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor contained in the moist air. They are fueled by a different heat mechanism than other cyclonic windstorms such as Nor'easters, European windstorms and polar lows, leading to their classification as "warm core" storm systems. Most tropical cyclones originate in the doldrums, approximately ten degrees from the Equator.
The term "tropical" refers to both the geographic origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively in tropical regions of the globe, as well as to their formation in maritime tropical air masses. The term "cyclone" refers to such storms' cyclonic nature, with anticlockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise rotation in the Southern Hemisphere. Depending on its location and intensity, a tropical cyclone may be referred to by names such as "hurricane", "typhoon", "tropical storm", "cyclonic storm", "tropical depression" or simply "cyclone".
Types of cyclone: 1. A "Typhoon" is a tropical cyclone located in the North-west Pacific Ocean which has the most cyclonic activity and storms occur year-round. 2. A "Hurricane" is also a tropical cyclone located at the North Atlantic Ocean or North-east Pacific Ocean which have an average storm activity and storms typically form between May 15 and November 30. 3. A "Cyclone" is a tropical cyclone that occurs in the South Pacific and Indian Oceans.
Selected named cyclone -
Hurricane Helene (/hɛˈliːn/ ⓘ heh-LEEN) was a deadly and devastating tropical cyclone that caused widespread catastrophic damage and numerous fatalities across the Southeastern United States in late September 2024. It was the strongest hurricane on record to strike the Big Bend region of Florida, the deadliest Atlantic hurricane since Maria in 2017, and the deadliest to strike the mainland U.S. since Katrina in 2005.
The eighth named storm, fifth hurricane, and second major hurricane of the 2024 Atlantic hurricane season, Helene began forming on September 22, 2024 as a broad low-pressure system in the western Caribbean Sea. By September 24, the disturbance had consolidated enough to become a tropical storm as it approached the Yucatán Peninsula, receiving the name Helene from the National Hurricane Center. Weather conditions led to the cyclone's intensification, and it became a hurricane early on September 25. More pronounced and rapid intensification ensued as Helene traversed the Gulf of Mexico the following day, reaching Category 4 intensity on the evening of September 26. Late on September 26, Helene made landfall at peak intensity in the Big Bend region of Florida, near the city of Perry, with maximum sustained winds of 140 mph (220 km/h). Helene weakened as it moved quickly inland before degenerating to a post-tropical cyclone over Tennessee on September 27. The storm then stalled over the state before dissipating on September 29. (Full article...)
Selected article -
Subtropical Storm Four brushed Florida and The Bahamas in October 1974. The eighteenth cyclone and fourth subtropical storm of the 1974 Atlantic hurricane season, the storm developed near eastern Cuba on October 4 from an area of disturbed weather. Shortly before striking Andros Island on October 6, the system strengthened into a subtropical storm. The storm made its closest approach to Florida early on October 7. Peaking with sustained winds of 50 mph (85 km/h), the system veered northward and then northeastward, but nonetheless caused heavy rainfall and coastal flooding on land in Florida. While paralleling offshore North Carolina and South Carolina, the storm began to slowly weaken. By late on October 8, the subtropical cyclone merged with a cold front while well east of Cape Hatteras.
Gale-force winds were observed by ships and land stations in The Bahamas. The storm and a stationary high pressure system over the Eastern United States resulted in strong winds and rough seas along the coast of Florida for several days, especially on October 6. Many coastal areas observed sustained winds of 25 to 40 mph (40 to 64 km/h), with higher gusts. The storm also produced isolated pockets of heavy rainfall, including 14 in (360 mm) of precipitation in Boca Raton. Dozens of homes were flooded in Boca Raton and Pompano Beach. The heavy rainfall destroyed about 50% of winter vegetable crops in Broward County and about 25% of the eggplant crop and about 5%–10% of other crops in Palm Beach County. The storm also brought rainfall and abnormally high tides to Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Bermuda. Damage totaled at least $600,000 (1974 USD). (Full article...)
Selected image -

Selected season -

The 2007–08 Australian region cyclone season was a slightly below-average tropical cyclone season. The season began with an early start, with the formation of the first tropical cyclone on 29 July, which was only recognized as a tropical cyclone during post-season analysis. This was the second time that a tropical cyclone had formed during July. The other one was Cyclone Lindsay in the 1996–1997 season. The next tropical cyclone that formed was Cyclone Guba, which formed on 13 November with TCWC Port Moresby assigning the name Guba on 14 November, which was the first named storm within TCWC Port Moresby's area of responsibility since Cyclone Epi in June 2003. Guba was also the first cyclone to occur in the Queensland region in November since 1977.
Tropical Cyclone Lee also formed on 13 November and was named by TCWC Perth on 14 November, with the system moving into RSMC Réunion's area of responsibility and being renamed Ariel. The next Cyclone to form within the Australian region was Melanie, which formed on 27 December and was named on the 28th by TCWC Perth. Melanie was the first storm of the season to require cyclone watches, and warnings were issued for the Pilbara coast, but it had weakened into a low-pressure area before it made landfall. (Full article...)
Related portals
Currently active tropical cyclones
Italicized basins are unofficial.
- North Atlantic (2025)
- No active systems
- East and Central Pacific (2025)
- No active systems
- West Pacific (2025)
- No active systems
- North Indian Ocean (2025)
- No active systems
- Mediterranean (2024–25)
- No active systems
- South-West Indian Ocean (2024–25)
- No active systems
- Australian region (2024–25)
- No active systems
- South Pacific (2024–25)
- No active systems
- South Atlantic (2024–25)
- No active systems
Last updated: 12:17, 16 May 2025 (UTC)
Tropical cyclone anniversaries

May 18
- 1986 - Cyclone Namu moved through the Solomon Islands, killing at least 111 people.
- 1997 - A powerful cyclone made landfall over in Bangladesh as a powerful Category 4 cyclone, killing more than 1,150 people.
- 2020 - Cyclone Amphan (pictured) reached peak intensity as a Category 5 super cyclonic storm, and two days later moved ashore near the border of India and Bangladesh. With an estimated US$13.7 billion in damages, Amphan was the costliest North Indian Ocean tropical cyclone on record.

May 19
- 1997 - A powerful cyclone (pictured) struck Bangladesh, killing 1,146 people.
- 2004 - A cyclone made landfall in Burma, causing floods and resulting in 236 fatalities.
- 2018 - Cyclone Sagar moved ashore Somaliland, with its associated floods killing 79 people across the region.

May 20
- 1989 - Typhoon Brenda makes landfall over Southern China as a Category 1 typhoon, killing about 84 people.
- 1999 - A powerful cyclone (pictured) struck southeastern Pakistan, killing at least 400 people, and perhaps as many as 6,000.
- 2005 - Tropical Depression Adrian became the first Pacific tropical cyclone to strike the Pacific coast of Honduras.
Did you know…


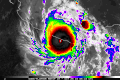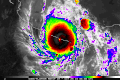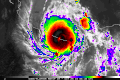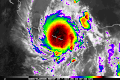
- …that the Joint Typhoon Warning Center considers that Typhoon Vera (pictured) of 1986 is actually two distinct systems, formed from two separated low-level circulations?
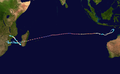
- …that Cyclone Freddy (track pictured) in 2023 was the longest-lasting tropical cyclone recorded?
- …that the typhoons of 2024—Yinxing, Toraji, Usagi, and Man-yi (pictured)—made history as the first recorded instance since 1951 of four tropical cyclones coexisting in November?
- …that Hurricane Otis (pictured) in 2023 was the first Pacific hurricane to make landfall at Category 5 intensity and surpassed Hurricane Patricia as the strongest landfalling Pacific hurricane on record?
General images -

The British Overseas Territory of Bermuda has a long history of encounters with Atlantic tropical cyclones, many of which inflicted significant damage and influenced the territory's development. A small archipelago comprising about 138 islands and islets, Bermuda occupies 21 square miles (54 km2) in the North Atlantic Ocean, roughly 650 miles (1,050 km) east of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina. The islands are situated far outside the Main Development Region for Atlantic hurricanes, but within the typical belt of recurving tropical cyclones. Most storms form in the central Atlantic or western Caribbean Sea before approaching Bermuda from the southwest; storms forming north of 28°N are unlikely to impact the territory.
According to the Bermuda Weather Service, Bermuda experiences a damaging tropical cyclone once every six to seven years, on average. Due to the small area of the island chain, landfalls and direct hits are rare. Strictly speaking, only 11 landfalls have occurred during years included in the official Atlantic hurricane database, starting in 1851.[1] When hurricanes Fay and Gonzalo struck Bermuda just days apart in October 2014, that season became the first to produce two landfalls. Two damaging storms impacted Bermuda in September 1899, but the center of the first narrowly missed the islands. Tropical cyclones, and their antecedent or remnant weather systems, have affected the territory in all seasons, most frequently in the late summer months. A study of recorded storms from 1609 to 1996 found that direct hits from hurricanes were most common in early September and late October, with an intervening relative lull creating two distinct 'seasons'. (Full article...)
Topics
Subcategories
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Tropical cyclones is the central point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of tropical cyclones. Feel free to help!
WikiProject Weather is the main center point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of meteorology in general, and the parent project of WikiProject Tropical cyclones. Three other branches of WikiProject Weather in particular share significant overlaps with WikiProject Tropical cyclones:
- The Non-tropical storms task force coordinates most of Wikipedia's coverage on extratropical cyclones, which tropical cyclones often transition into near the end of their lifespan.
- The Floods task force takes on the scope of flooding events all over the world, with rainfall from tropical cyclones a significant factor in many of them.
- WikiProject Severe weather documents the effects of extreme weather such as tornadoes, which landfalling tropical cyclones can produce.
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
- ^ "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)" (Database). United States National Hurricane Center. May 11, 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- Landsea, Chris (April 2022). "The revised Atlantic hurricane database (HURDAT2) - Chris Landsea – April 2022" (PDF). Hurricane Research Division – NOAA/AOML. Miami: Hurricane Research Division – via Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search















































