Back بوابة:علم الفيروسات Arabic درگاه:ویروس Persian Portail:Virologie French Portal:Virus ID Portal:Vírus Portuguese ද්වාරය:වෛරස Singhalese باب:وائرسز Urdu Portal:病毒 Chinese
The Viruses Portal
Welcome!
Viruses are small infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all forms of life, including animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and archaea. They are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most abundant type of biological entity, with millions of different types, although only about 6,000 viruses have been described in detail. Some viruses cause disease in humans, and others are responsible for economically important diseases of livestock and crops.
Virus particles (known as virions) consist of genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA, wrapped in a protein coat called the capsid; some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope. The capsid can take simple helical or icosahedral forms, or more complex structures. The average virus is about 1/100 the size of the average bacterium, and most are too small to be seen directly with an optical microscope.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids, others from bacteria. Viruses are sometimes considered to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce and evolve through natural selection. However they lack key characteristics (such as cell structure) that are generally considered necessary to count as life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life".
Selected disease
Yellow fever is an acute haemorrhagic fever caused by the yellow fever virus, an RNA virus in the Flaviviridae family. It infects humans, other primates, and Aedes aegypti and other mosquito species, which act as the vector. After transmission by the bite of a female mosquito, the virus replicates in lymph nodes, infecting dendritic cells, and can then spread to liver hepatocytes. Symptoms generally last 3–4 days, and include fever, nausea and muscle pain. In around 15% of people, a toxic phase follows with recurring fever, liver damage and jaundice, sometimes accompanied by bleeding and kidney failure; death occurs in 20–50% of those who develop jaundice. Infection otherwise leads to lifelong immunity.
The first definitive outbreak of yellow fever was in Barbados in 1647, and major epidemics have occurred in the Americas and southern Europe since that date. Yellow fever is endemic in tropical and subtropical areas of South America and Africa; its incidence has been increasing since the 1980s. An estimated 200,000 cases and 30,000 deaths occur each year, with almost 90% of cases being in Africa. Antiviral therapy is not effective. A vaccine is available, and vaccination, mosquito control and bite prevention are the main preventive measures.
Selected image
The first immortal human cell line, HeLa cells were derived from a cervical cancer biopsy and carry human papillomavirus 18 DNA. The cells have been growing since 1951.
Credit: Gerry Shaw (8 March 2012)
In the news
26 February: In the ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), more than 110 million confirmed cases, including 2.5 million deaths, have been documented globally since the outbreak began in December 2019. WHO
18 February: Seven asymptomatic cases of avian influenza A subtype H5N8, the first documented H5N8 cases in humans, are reported in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia, after more than 100,0000 hens died on a poultry farm in December. WHO
14 February: Seven cases of Ebola virus disease are reported in Gouécké, south-east Guinea. WHO
7 February: A case of Ebola virus disease is detected in North Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. WHO
4 February: An outbreak of Rift Valley fever is ongoing in Kenya, with 32 human cases, including 11 deaths, since the outbreak started in November. WHO
21 November: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gives emergency-use authorisation to casirivimab/imdevimab, a combination monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy for non-hospitalised people twelve years and over with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, after granting emergency-use authorisation to the single mAb bamlanivimab earlier in the month. FDA 1, 2
18 November: The outbreak of Ebola virus disease in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, which started in June, has been declared over; a total of 130 cases were recorded, with 55 deaths. UN
Selected article
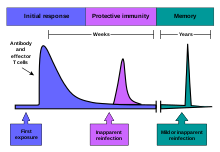
The immune system is a system of structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. It must detect a wide variety of pathogens – from viruses to parasitic worms – distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue, and neutralise them. Simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria have enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms, including phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system, evolved in ancient eukaryotes and are found in plants and invertebrates.
Humans and most other vertebrates have more sophisticated defence mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognise specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Viruses and other pathogens can rapidly evolve to evade immune detection, and some viruses, notably HIV, cause the immune system to function less effectively.
Selected outbreak
The West African Ebola epidemic was the most widespread outbreak of the disease to date. Beginning in Meliandou in southern Guinea in December 2013, it spread to adjacent Liberia and Sierra Leone, affecting the cities of Conakry and Monrovia, with minor outbreaks in Mali and Nigeria. Cases reached a peak in October 2014 and the epidemic was under control by late 2015, although occasional cases continued to occur into April 2016. Ring vaccination with the then-experimental vaccine rVSV-ZEBOV was trialled in Guinea.
More than 28,000 suspected cases were reported with more than 11,000 deaths; the case fatality rate was around 40% overall and around 58% in hospitalised patients. Early in the epidemic nearly 10% of the dead were healthcare workers. The outbreak left about 17,000 survivors, many of whom reported long-lasting post-recovery symptoms. Extreme poverty, dysfunctional healthcare systems, distrust of government after years of armed conflict, local burial customs of washing the body, the unprecedented spread of Ebola to densely populated cities, and the delay in response of several months all contributed to the failure to control the epidemic.
Selected quotation
| “ | There is no question that virology has long outgrown the confines of "Microbiology": it is an important discipline in its own right, a fact that is attested by the numerous high quality journals that are exclusively devoted to it. Further, it is primarily virology that has made possible the rapid rise of molecular cell biology. | ” |
—Bill Joklik on founding a society for virology
Recommended articles
Viruses & Subviral agents: bat virome • elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus • HIV • introduction to viruses![]() • Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus
• Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus![]() • virus
• virus![]()
Diseases: colony collapse disorder • common cold • croup • dengue fever![]() • gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza
• gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza![]() • meningitis
• meningitis![]() • myxomatosis • polio
• myxomatosis • polio![]() • pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
• pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
Epidemiology & Interventions: 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak • Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations • Disease X • 2009 flu pandemic • HIV/AIDS in Malawi • polio vaccine • Spanish flu • West African Ebola virus epidemic
Virus–Host interactions: antibody • host • immune system![]() • parasitism • RNA interference
• parasitism • RNA interference![]()
Methodology: metagenomics
Social & Media: And the Band Played On • Contagion • "Flu Season" • Frank's Cock![]() • Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa
• Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa![]() • social history of viruses
• social history of viruses![]() • "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
• "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
People: Brownie Mary • Macfarlane Burnet![]() • Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C
• Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C![]() • HIV-positive people
• HIV-positive people![]() • Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock
• Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock![]() • poliomyelitis survivors
• poliomyelitis survivors![]() • Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White
• Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White![]()
Selected virus
Alphaviruses are a genus of RNA viruses in the Togaviridae family. The spherical enveloped virion is 70 nm in diameter, with a nucleocapsid of 40 nm. It has a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome of 11–12 kb. The genus contains more than thirty species, which infect humans, horses, rodents and other mammals, as well as fish, birds, other vertebrates and invertebrates. Alphaviruses are generally transmitted by insect vectors, predominantly mosquitoes, and are an example of arboviruses (arthropod-borne viruses).
The first alphavirus to be discovered was western equine encephalitis virus, by Karl Friedrich Meyer in 1930, in horses with fatal encephalitis in San Joaquin Valley, California, USA. Some members of the genus cause significant disease in humans, including the chikungunya, o'nyong'nyong, Ross River, Sindbis, Barmah Forest and Semliki Forest (pictured) viruses and the eastern, western and Venezuelan equine encephalitis viruses. Arthritis, encephalitis, rashes and fever are the most frequently observed symptoms. Large mammals such as humans usually form dead-end hosts for the viruses, although Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus is mainly amplified in the horse. No human vaccine or antiviral drug has been licensed. Prevention is predominantly by control of the insect vector.
Did you know?
- ...that the greenbug (pictured) is the vector of several plant viruses?
- ...that during the West African Ebola virus epidemic as many as 15 different vaccines were in development?
- ...that in 1978, populations of the gulf sea star in the Gulf of California were devastated by starfish wasting disease and had not fully recovered twenty years later?
- ...that virologist Stephen Straus, first head of the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine, said he did not use alternative medicine?
- ...that Looking for Madonna, meant to raise awareness of HIV/AIDS in Papua, used shots of a green bra to symbolise sex?
Selected biography
George Keble Hirst (2 March 1909 – 22 January 1994) was an American virologist who was among the first to study the molecular biology and genetics of animal viruses.
Hirst started to work on influenza virus in 1940, only a few years after it had been isolated. He soon discovered that the virus caused red blood cells to clump together. This phenomenon could be used to diagnose influenza, which had previously required growing the virus in ferrets. He invented the haemagglutination assay, a simple method for quantifying viruses, and later the haemagglutination inhibition assay, which measures virus-specific antibodies in serum. In 1942, he discovered the neuraminadase enzyme, showing for the first time that viruses could contain enzymes. Neuraminidase is the target of the neuraminidase inhibitor class of antiviral drugs, including oseltamivir and zanamivir. In 1962, he was also the first to propose the then-revolutionary idea that virus genomes can consist of discontinuous segments.
He co-founded Virology in 1955, the first English-language journal to focus on viruses, and directed the Public Health Research Institute in New York City for nearly 25 years (1956–81).
In this month
1 September 1910: Peyton Rous shows that a sarcoma of chickens, subsequently associated with Rous sarcoma virus, is transmissible
3 September 1917: Discovery of bacteriophage of Shigella by Félix d'Herelle
8 September 1976: Death of Mabalo Lokela, the first known case of Ebola virus
8 September 2015: Discovery of giant virus Mollivirus sibericum in Siberian permafrost
11 September 1978: Janet Parker was the last person to die of smallpox
12 September 1957: Interferon discovered by Alick Isaacs and Jean Lindenmann
12 September 1985: Structure of human rhinovirus 14 (pictured) solved by Michael Rossmann and colleagues, the first atomic-level structure of an animal virus
17 September 1999: Jesse Gelsinger died in a clinical trial of gene therapy using an adenovirus vector, the first known death due to gene therapy
20 September 2015: Wild poliovirus type 2 declared eradicated
26 September 1997: Combivir (zidovudine/lamivudine) approved; first combination antiretroviral
27 September 1985: Structure of poliovirus solved by Jim Hogle and colleagues
28 September 2007: First World Rabies Day is held
Selected intervention
Zidovudine (ZDV) (also known as AZT and sold as Retrovir) is an antiretroviral drug used in the prevention and treatment of HIV/AIDS. Classed as a nucleoside analogue reverse-transcriptase inhibitor, it inhibits HIV's reverse transcriptase enzyme, which copies the viral RNA into DNA and is essential for its replication. The first breakthrough in AIDS therapy, ZDV was licensed in 1987. While it significantly reduces HIV replication, leading to some clinical and immunological benefits, when used alone ZDV does not completely stop replication, allowing the virus to become resistant to it. The drug is therefore used together with other anti-HIV drugs in combination therapy called highly active antiretroviral therapy. To simplify its administration, ZDV is included in combination pills with lamivudine (Combivir) and lamivudine plus abacavir (Trizivir). ZDV continues to be used to prevent HIV transmission from mother to child during childbirth; it was previously part of the standard post-exposure prophylaxis after needlestick injury.
Subcategories
Subcategories of virology:
Topics
Things to do
- Comment on what you like and dislike about this portal
- Join the Viruses WikiProject
- Tag articles on viruses and virology with the project banner by adding {{WikiProject Viruses}} to the talk page
- Assess unassessed articles against the project standards
- Create requested pages: red-linked viruses | red-linked virus genera
- Expand a virus stub into a full article, adding images, citations, references and taxoboxes, following the project guidelines
- Create a new article (or expand an old one 5-fold) and nominate it for the main page Did You Know? section
- Improve a B-class article and nominate it for Good Article
 or Featured Article
or Featured Article status
status - Suggest articles, pictures, interesting facts, events and news to be featured here on the portal
WikiProjects & Portals
 WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
Medicine • Microbiology • Molecular & Cellular Biology • Veterinary Medicine
Related PortalsAssociated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search