
Back Societat protoindoeuropea Catalan Sociedad protoindoeuropea Spanish Società protoindoeuropea Italian Sociedade protoindo-europeia Portuguese
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| Part of a series on |
| Indo-European topics |
|---|
 |
|
|
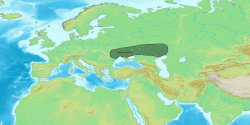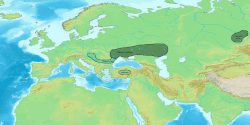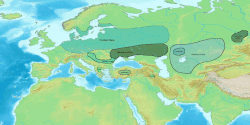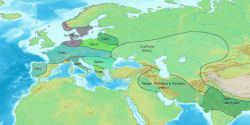
Proto-Indo-European society is the reconstructed culture of Proto-Indo-Europeans, the ancient speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language, ancestor of all modern Indo-European languages. Historical linguistics combined with archaeological and genetic evidence have provided the current basis for understanding the culture and its people. The most widely-accepted theory suggests that the culture emerged on the Pontic-Caspian steppe after 5000 BCE, a period known as the Chalcolithic where smelted copper and stone tools were in use simultaneously. Proto-Indo-European speakers are considered to have been semi-nomadic, but domestication of cattle, first for ritual sacrifice and later for consumption, dairy production, and cereal cultivation emerged as the culture shifted from herding and hunter-gatherer to farming. The social hierarchy included an upper class of priests, warriors, and tribe chiefs, a lower class of commoners, and slaves; patrilineality and patriarchy characteristics have been well-established. Trade, bolstered by access to wheeled wagons, connected Proto-Indo-European culture to others with archaeological and linguistic evidence supporting relations with Proto-Uralic peoples, Uruk, and Old European cultures.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search