
Back Ditón Czech Ditonus German Ditono Esperanto Ditono Spanish فاصله فیثاغورثی Persian Ditonus Dutch Дитон Russian 畢氏音程 Chinese
The article's lead section may need to be rewritten. (November 2010) |
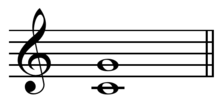
In musical tuning theory, a Pythagorean interval is a musical interval with a frequency ratio equal to a power of two divided by a power of three, or vice versa.[1] For instance, the perfect fifth with ratio 3/2 (equivalent to 31/ 21) and the perfect fourth with ratio 4/3 (equivalent to 22/ 31) are Pythagorean intervals.
All the intervals between the notes of a scale are Pythagorean if they are tuned using the Pythagorean tuning system. However, some Pythagorean intervals are also used in other tuning systems. For instance, the above-mentioned Pythagorean perfect fifth and fourth are also used in just intonation.
- ^ Benson, Donald C. (2003). A Smoother Pebble: Mathematical Explorations, p.56. ISBN 978-0-19-514436-9. "The frequency ratio of every Pythagorean interval is a ratio between a power of two and a power of three...confirming the Pythagorean requirements that all intervals be associated with ratios of whole numbers."
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search