Back مضلع منتظم Arabic সমবহুভুজ Assamese Düzgün çoxbucaqlı Azerbaijani Правилен многоъгълник Bulgarian সুষম বহুভুজ Bengali/Bangla فرەگۆشەی ڕێک CKB Pravidelný mnohoúhelník Czech Тĕрĕс нумайкĕтеслĕх CV Polygon rheolaidd Welsh Regelmäßiges Polygon German
| Edges and vertices | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schläfli symbol | |||||||||||||
| Coxeter–Dynkin diagram | |||||||||||||
| Symmetry group | Dn, order 2n | ||||||||||||
| Dual polygon | Self-dual | ||||||||||||
| Area (with side length ) | |||||||||||||
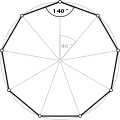
| Internal angle | |||||||||||||
| Internal angle sum | |||||||||||||
| Inscribed circle diameter | |||||||||||||
| Circumscribed circle diameter | |||||||||||||
| Properties | Convex, cyclic, equilateral, isogonal, isotoxal | ||||||||||||
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either convex or star. In the limit, a sequence of regular polygons with an increasing number of sides approximates a circle, if the perimeter or area is fixed, or a regular apeirogon (effectively a straight line), if the edge length is fixed.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search