
Back Relê Afrikaans مرحل Arabic Relé AST Rele Azerbaijani Рэле Byelorussian Реле Bulgarian রিলে Bengali/Bangla Relé Catalan Elektromagnetické relé Czech Relæ Danish

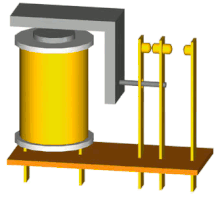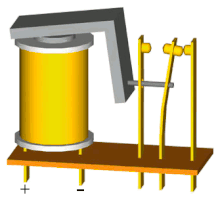

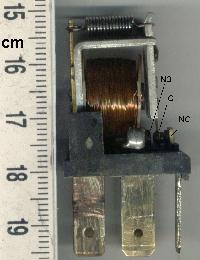
A relay is an electrically operated switch. It consists of a set of input terminals for a single or multiple control signals, and a set of operating contact terminals. The switch may have any number of contacts in multiple contact forms, such as make contacts, break contacts, or combinations thereof.
Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by an independent low-power signal, or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. Relays were first used in long-distance telegraph circuits as signal repeaters: they refresh the signal coming in from one circuit by transmitting it on another circuit. Relays were used extensively in telephone exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations.
The traditional electromechanical form of a relay uses an electromagnet to close or open the contacts, but relays using other operating principles have also been invented, such as in solid-state relays which use semiconductor properties for control without relying on moving parts. Relays with calibrated operating characteristics and sometimes multiple operating coils are used to protect electrical circuits from overload or faults; in modern electric power systems these functions are performed by digital instruments still called protective relays or safety relays.
Latching relays require only a single pulse of control power to operate the switch persistently. Another pulse applied to a second set of control terminals, or a pulse with opposite polarity, resets the switch, while repeated pulses of the same kind have no effects. Magnetic latching relays are useful in applications when interrupted power should not affect the circuits that the relay is controlling.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search