
Back لغة رومانيولية Arabic لغه رومانيولو ARZ Dialeutu romañol AST Romagnol German Lengua rumagnòla EML Dialecto romañol Spanish Romagnolin kieli Finnish Romagnol French Romagnol FRR Romanjolski jezik Croatian
| Romagnol | |
|---|---|
| Rumagnòl | |
| Pronunciation | [rumɐˈɲoːl]/[rumɐˈɲoə̯l] |
| Native to | Italy, San Marino |
| Region | Primarily Emilia-Romagna, San Marino, Marche |
| Ethnicity | 1.1 million (2008)[1] |
Native speakers | Unknown, c. 430,000, assuming Romagnol and Emilian retained at same rate (2006)[2] |
| Dialects | Ravennate Forlivese Faentino Cesenate Riminese Sammarinese Gallo-Picene (disputed) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | rgn |
| Glottolog | roma1328 |
| ELP | Romagnol |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-oki ... okl |
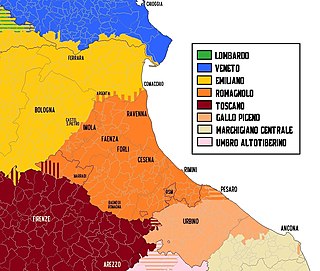 Linguistic map of Romagna and neighbouring regions[image reference needed] | |
 Romagnol is classified as Definitely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
Romagnol (rumagnòl or rumagnôl; Italian: romagnolo) is a Romance language spoken in the historical region of Romagna, consisting mainly of the southeastern part of Emilia-Romagna, Italy. The name is derived from the Lombard name for the region, Romagna.[3] Romagnol is also spoken outside the region, particularly in the independent Republic of San Marino.[4] Romagnol is classified as endangered because older generations have "neglected to pass on the dialect as a native tongue to the next generation".[5]
- ^ Miani, Ivan (2008-04-12). "ISO 639-3 Registration Authority Request for New Language Code Element in ISO 639-3" (PDF). ISO 639-3.
- ^ "La lingua italiana, i dialetti e le lingue straniere Anno 2006" [The Italian language, dialects and foreign languages Year 2006] (PDF) (in Italian). 2006.
- ^ Larner, J. (1965). The Lords of Romagna: Romagnol Society and the Origins of the Signorie. Ithaca: New York.
- ^ Grementieri, S. (2012, January 7). The Romagnolo Dialect: A Short Study On its History, Grammar, and How it Survives [Scholarly project]. In www.dialettoromagnolo.it. Retrieved March 4, 2017, from http://www.dialettoromagnolo.it/uploads/5/2/4/2/52420601/pb-241-file-grementieri_the_romagnolo_dialect.pdf
- ^ Cenni, I. (2013). Code-switching as an indicator of language shift: a case study of the Romagnolo dialect of Gatteo a Mare, Italy. 46th International Annual Meeting of the Societas Linguistica Europaea, Abstracts. Presented at the 46th International Annual Meeting of the Societas Linguistica Europaea.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search