
Back كييس (تشريح) Arabic Sakulus BS Sàcul Catalan Kulovitý váček Czech Sáculo Spanish Sakulu Basque Sacculus dan utriculus ID Sacculo Italian 둥근주머니 Korean Woreczek Polish
| Saccule | |
|---|---|
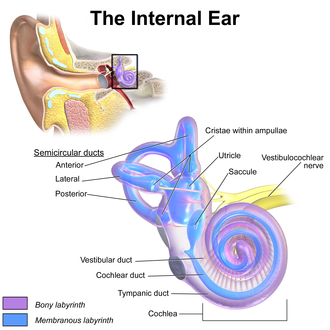 Inner ear, showing saccule near center. | |
 illustration of otolith organs showing detail of utricle, otoconia, endolymph, cupula, macula of saccule, hair cell filaments, and saccular nerve | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Inner ear |
| System | Balance |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sacculus |
| TA98 | A15.3.03.065 |
| TA2 | 7001 |
| FMA | 61116 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The saccule (Latin: sacculus) is a bed of sensory cells in the inner ear. The saccule is from Latin saccus 'sack'. The saccule translates head movements into neural impulses for the brain to interpret. The saccule detects linear accelerations and head tilts in the vertical plane. When the head moves vertically, the sensory cells of the saccule are disturbed and the neurons connected to them begin transmitting impulses to the brain. These impulses travel along the vestibular portion of the eighth cranial nerve to the vestibular nuclei in the brainstem.
The vestibular system is important in maintaining balance, or equilibrium. The vestibular system includes the saccule, utricle, and the three semicircular canals. The vestibule is the name of the fluid-filled, membranous duct that contains these organs of balance. The vestibule is encased in the temporal bone of the skull.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search