
Back حصار بغداد (1733) Arabic Bağdadın mühasirəsi (1733) Azerbaijani Asedio de Bagdad (1733) Spanish محاصره بغداد (۱۷۳۳) Persian Assedio di Baghdad (1733) Italian ბაღდადის ალყა (1733) Georgian Осада Багдада (1733) Russian Bağdat Kuşatması (1733) Turkish
| Siege of Baghdad | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Ottoman–Persian War (1730–35) and Nader's Campaigns | |||||||
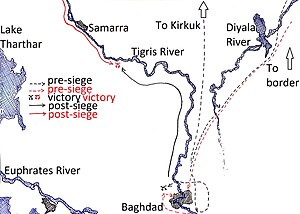 The campaign in the Eyalat of Baghdad from Nader's invasion up to his defeat at Samarra which resulted in the lifting of the siege of Baghdad. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Nader Mohammad Khan Baluch |
Ahmad Pasha Topal Pasha | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
100,000
| Unknown | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Heavy | Heavy | ||||||
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2024) |
The siege of Baghdad (1733) was a relatively short but intense siege of Ottoman-held Baghdad by the Persian army under Nader. The outcome was determined not at Baghdad but ultimately far to the north near Samara where a large relief force commanded by the Topal Pasha inflicted a decisive defeat on Nader's Persian army (the only battlefield defeat of Nader's career). The Persian besiegers were forced away with the loss of most of their equipment and saving a much exhausted garrison desperate for relief.
- ^ Ghafouri, Ali(2008). History of Iran's wars: from the Medes to now, Etela'at Publishing[verification needed]
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search