
Back সুইং (জাভা) Bengali/Bangla Swing (Java) Catalan Swing (Java) Czech Swing (Java) German Swing (biblioteca gráfica) Spanish Swing (Java) Finnish Swing (Java) French Swing HE Swing Armenian Swing (Java) Italian
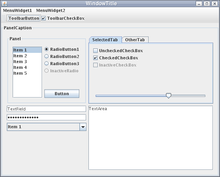
Swing is a GUI widget toolkit for Java.[1] It is part of Oracle's Java Foundation Classes (JFC) – an API for providing a graphical user interface (GUI) for Java programs.
Swing was developed to provide a more sophisticated set of GUI components than the earlier Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT). Swing provides a look and feel that emulates the look and feel of several platforms, and also supports a pluggable look and feel that allows applications to have a look and feel unrelated to the underlying platform. It has more powerful and flexible components than AWT. In addition to familiar components such as buttons, check boxes and labels, Swing provides several advanced components such as tabbed panel, scroll panes, trees, tables, and lists.[2]
Unlike AWT components, Swing components are not implemented by platform-specific code. Instead, they are written entirely in Java and therefore are platform-independent.
In December 2008, Sun Microsystems (Oracle's predecessor) released the CSS / FXML based framework that it intended to be the successor to Swing, called JavaFX.[3]
- ^ "What is Java Swing? - Definition from Techopedia". Techopedia Inc. Retrieved 2018-11-03.
- ^ Yap, Chee (2003-04-30). "JAVA SWING GUI TUTORIAL". New York University (NYU). Retrieved 2018-11-03.
- ^ "Developing a basic GUI application using JavaFX in Eclipse". July 2017.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search