
Back المعاهدة المنشئة لآلية الاستقرار الأوروبي Arabic Verdrag tot oprichting van het Europees Stabiliteitsmechanisme Dutch
| Treaty Establishing the European Stability Mechanism | |
|---|---|
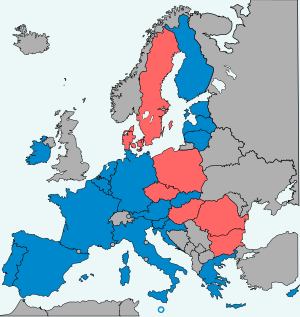 ESM member states Other EU member states | |
| Type | Intergovernmental agreement |
| Signed | 2 February 2012 |
| Location | Brussels |
| Effective | 27 September 2012[1][2] |
| Condition | Ratification by signatories whose initial subscriptions represent no less than 90% of the total |
| Parties | All Member States of the eurozone (20) |
| Depositary | General Secretariat of the Council of the European Union |
| Languages | Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Irish, Italian, Maltese, Portuguese, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish and Swedish |
| Full text | |
The Treaty Establishing the European Stability Mechanism was signed by the member states of the eurozone to found the European Stability Mechanism (ESM), an international organisation located in Luxembourg, to act as a permanent source of financial assistance for member states in financial difficulty, with a maximum lending capacity of €500 billion. It replaced two earlier temporary EU funding programmes: the European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) and the European Financial Stabilisation Mechanism (EFSM). All new bailouts of eurozone member states will be covered by ESM, while the EFSF and EFSM will continue to handle money transfers and program monitoring for bailouts previously approved for Ireland, Portugal and Greece.
The treaty stipulated that the organization would be established if member states representing 90% of its original capital requirements ratified the founding treaty.[3] This threshold was surpassed with Germany's ratification on 27 September 2012, bringing the treaty into force on that date for the sixteen states which had ratified the agreement. The ESM commenced its operations at a meeting on 8 October 2012.[4] A separate treaty, amending Article 136 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU) to authorize the establishment of the ESM under EU law, was planned to enter into force on 1 January 2013. However, the last of the 27 European Union member states to ratify the amendment, the Czech Republic, did not do so until 23 April 2013, resulting in its entry into force on 1 May 2013.[5] In June 2015, an updated EMU reform plan was released which envisaged that in the medium-term (between July 2017 and 2025) the ESM should be transposed from being an intergovernmental agreement to become fully integrated into the EU law framework applying to all eurozone member states, so that the ESM can be governed more smoothly by the EU institutions - under the competence provided for by the amended article 136 of the TFEU.[6]
- ^ The treaty entered into force for 16 signatories on 27 September 2012, and Estonia on 4 October 2012
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ESM TREATYwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "European Council Press releases". European Council. 9 December 2011. Retrieved 9 December 2011.
- ^ "Germany finally ratifies ESM bailout fund". 27 September 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2012.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Deposit of TFEU article 136 amendmentwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Completing Europe's Economic and Monetary Union: Report by Jean-Claude Juncker in close cooperation with Donald Tusk, Jeroen Dijsselbloem, Mario Draghi and Martin Schulz" (PDF). European Commission. 21 June 2015.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search