
Back بنية جزيئية هرمية مزدوجة ثلاثية Arabic Geometría molecular bipiramidal trigonal Spanish هندسه مولکولی دو هرمی مثلثی Persian Géométrie moléculaire bipyramidale trigonale French Geometri molekul bipiramida segitiga ID 三方両錐形分子構造 Japanese Trigonaal bipiramidale moleculaire geometrie Dutch Trigonal bipyramidal geometri Swedish Тригонально-біпірамідальна структура Ukrainian 双三角锥形分子构型 Chinese
| Trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry | |
|---|---|
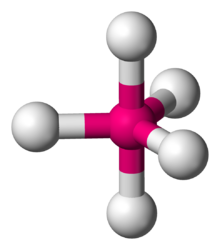 | |
| Examples | PF5, Fe(CO)5 |
| Point group | D3h |
| Coordination number | 5 |
| Bond angle(s) | 90°, 120° |
| μ (Polarity) | 0 |
In chemistry, a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular bipyramid.[1] This is one geometry for which the bond angles surrounding the central atom are not identical (see also pentagonal bipyramid), because there is no geometrical arrangement with five terminal atoms in equivalent positions. Examples of this molecular geometry are phosphorus pentafluoride (PF5), and phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) in the gas phase.[2]
- ^ "Trigonal bipyramidal molecules". Creative Chemistry. Retrieved 2023-02-07.
- ^ Housecroft, C. E.; Sharpe, A. G. (2004). Inorganic Chemistry (2nd ed.). Prentice Hall. p. 407. ISBN 978-0-13-039913-7.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search