
Back Uretra AN إحليل Arabic Sidik kanalı Azerbaijani Uretra BCL Мочаспускальны канал Byelorussian Мачаспуск BE-X-OLD Пикочен канал Bulgarian यूरेथ्रा Bihari মূত্রনালী Bengali/Bangla Mokraćna cijev BS
| Urethra | |
|---|---|
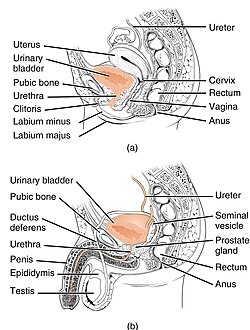 The urethra transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. This image shows (a) a human female urethra and (b) a human male urethra. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Urogenital sinus |
| Artery | Inferior vesical artery Middle rectal artery Internal pudendal artery |
| Vein | Inferior vesical vein Middle rectal vein Internal pudendal vein |
| Nerve | Pudendal nerve Pelvic splanchnic nerves Inferior hypogastric plexus |
| Lymph | Internal iliac lymph nodes Deep inguinal lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | urethra feminina (female); urethra masculina (male) |
| Greek | οὐρήθρα |
| MeSH | D014521 |
| TA98 | A08.4.01.001F A08.5.01.001M |
| TA2 | 3426, 3442 |
| FMA | 19667 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The urethra (pl.: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus,[1][2] through which placental mammals urinate and ejaculate.[3]
The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination.[4] The internal sphincter, formed by the involuntary smooth muscles lining the bladder neck and urethra, receives its nerve supply by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.[5] The internal sphincter is present both in males and females.[6][7][8]
- ^ Brading, Alison F. (January 1999). "The physiology of the mammalian urinary outflow tract". Experimental Physiology. 84 (1): 215–221. doi:10.1111/j.1469-445X.1999.tb00084.x. ISSN 0958-0670. PMID 10081719.
- ^ Lombardi, Julian (2012-12-06). Comparative Vertebrate Reproduction. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4615-4937-6.
- ^ Marvalee H. Wake (15 September 1992). Hyman's Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy. University of Chicago Press. pp. 583–. ISBN 978-0-226-87013-7. Retrieved 6 May 2013.
- ^ Legato, Marianne J.; Bilezikian, John P., eds. (2004). "109: The Evaluation and Treatment of Urinary Incontinence". Principles of Gender-specific Medicine. Vol. 1. Gulf Professional Publishing. p. 1187.
- ^ Chancellor, Michael B; Yoshimura, Naoki (2004). "Neurophysiology of Stress Urinary Incontinence". Reviews in Urology. 6 (Suppl 3): S19 – S28. PMC 1472861. PMID 16985861.
- ^ Jung, Junyang; Anh, Hyo Kwang; Huh, Youngbuhm (September 2012). "Clinical and Functional Anatomy of the Urethral Sphincter". International Neurourology Journal. 16 (3): 102–106. doi:10.5213/inj.2012.16.3.102. PMC 3469827. PMID 23094214.
- ^ Karam, I.; Moudouni, S.; Droupy, S.; Abd-Almasad, I.; Uhl, J. F.; Delmas, V. (April 2005). "The structure and innervation of the male urethra: histological and immunohistochemical studies with three-dimensional reconstruction". Journal of Anatomy. 206 (4): 395–403. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00402.x. PMC 1571491. PMID 15817107.
- ^ Ashton-Miller, J. A.; DeLancey, J. O. (April 2007). "Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1101 (1): 266–296. Bibcode:2007NYASA1101..266A. doi:10.1196/annals.1389.034. hdl:2027.42/72597. PMID 17416924. S2CID 6310287. Archived from the original on Aug 22, 2023 – via Deep Blue Documents.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search