
Back Mesón vectorial Spanish Méson vecteur French Векторные мезоны Russian Vektorski mezon Slovenian
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2021) |
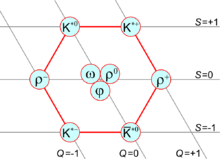
In high energy physics, a vector meson is a meson with total spin 1 and odd parity (usually noted as JP = 1−). Vector mesons have been seen in experiments since the 1960s, and are well known for their spectroscopic pattern of masses.[1]
The vector mesons contrast with the pseudovector mesons, which also have a total spin 1 but instead have even parity. The vector and pseudovector mesons are also dissimilar in that the spectroscopy of vector mesons tends to show nearly pure states of constituent quark flavors, whereas pseudovector mesons and scalar mesons tend to be expressed as composites of mixed states.
- ^ Nichitiu, F. (November 2, 1995). "An Introduction to the Vector Meson" (PDF). Retrieved June 1, 2021.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search