This article may be confusing or unclear to readers. In particular, the article uses many terms which are nowhere defined in Wikipedia, and are not commonly defined in modern mathematics: rectangular vector, spherical vectors, etc. Moreover, except for the lead, it is not about notation, but about the representation of vectors (or points?) by means of coordinates.. (January 2024) |
Vector notation
Vector components
Describing an arrow vector v by its coordinates x and y yields an isomorphism of vector spaces.
Describing an arrow vector v by its coordinates x and y yields an isomorphism of vector spaces.
Scalar product
Two equal-length sequences of coordinate vectors and returns a single number
Two equal-length sequences of coordinate vectors and returns a single number
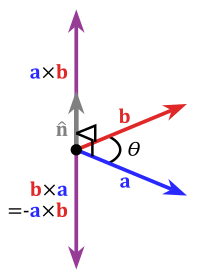
Vector product
The cross-product in respect to a right-handed coordinate system
The cross-product in respect to a right-handed coordinate system
In mathematics and physics, vector notation is a commonly used notation for representing vectors,[1][2] which may be Euclidean vectors, or more generally, members of a vector space.
For representing a vector, the common typographic convention is lower case, upright boldface type, as in v. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) recommends either bold italic serif, as in v, or non-bold italic serif accented by a right arrow, as in .[3]
In advanced mathematics, vectors are often represented in a simple italic type, like any variable.[citation needed]
- ^ Principles and Applications of Mathematics for Communications-electronics. 1992. p. 123.
- ^ Coffin, Joseph George (1911). Vector Analysis. J. Wiley & sons.
- ^ "ISO 80000-2:2019 Quantities and units — Part 2: Mathematics". International Organization for Standardization. August 2019.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search