
Back حوسبة الحافة Arabic Edge computing Czech Edge Computing German Computación frontera Spanish رایانش لبهای Persian Edge computing French Եզրային հաշվարկ Armenian Komputasi tepi ID Edge computing Italian エッジコンピューティング Japanese
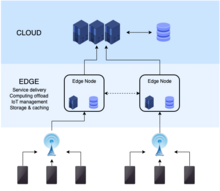
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that brings computation and data storage closer to the sources of data, so that a user is likely to be physically closer to a server than if all servers were in one place. This often makes applications faster.[1] More broadly, it refers to any design that pushes computation physically closer to a user, so as to reduce the latency compared to when an application runs on a single data centre.[2]
The term began being used in the 1990s to describe content delivery networks—these were used to deliver website and video content from servers located near users.[3] In the early 2000s, these systems expanded their scope to hosting other applications,[4] leading to early edge computing services.[5] These services could do things like find dealers, manage shopping carts, gather real-time data, and place ads.
The Internet of Things (IoT), where devices are connected to the internet, is often linked with edge computing. However, it's important to understand that edge computing and IoT are not the same thing.[6]
- ^ Hamilton, Eric (27 December 2018). "What is Edge Computing: The Network Edge Explained". cloudwards.net. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- ^ Gartner. "Gartner Trend Insights report 2018" (PDF). Gartner. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-12-18. Retrieved 2021-05-26.
- ^ "Globally Distributed Content Delivery, by J. Dilley, B. Maggs, J. Parikh, H. Prokop, R. Sitaraman and B. Weihl, IEEE Internet Computing, Volume 6, Issue 5, November 2002" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-08-09. Retrieved 2019-10-25.
- ^ Nygren., E.; Sitaraman R. K.; Sun, J. (2010). "The Akamai network: A platform for high-performance internet applications" (PDF). ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review. 44 (3): 2–19. doi:10.1145/1842733.1842736. S2CID 207181702. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 13, 2012. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
See Section 6.2: Distributing Applications to the Edge
- ^ Davis, A.; Parikh, J.; Weihl, W. (2004). "Edgecomputing: Extending enterprise applications to the edge of the internet". Proceedings of the 13th international World Wide Web conference on Alternate track papers & posters - WWW Alt. '04. p. 180. doi:10.1145/1013367.1013397. ISBN 1581139128. S2CID 578337.
- ^ Gartner. "2021 Strategic Roadmap for Edge Computing". www.gartner.com. Archived from the original on 2021-03-30. Retrieved 2021-07-11.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search