
Back Erfahrungskurve German اثر تجربه Persian Curva di esperienza Italian 経験曲線効果 Japanese 경험효과 Korean Leercurve (productie) Dutch Ефекти кривої досвіду Ukrainian 经验学习曲线 Chinese 經驗學習曲線 ZH-YUE
It has been suggested that this article be merged with Learning curve. (Discuss) Proposed since April 2024. |
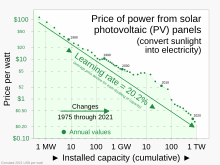
In industry, models of the learning or experience curve effect express the relationship between experience producing a good and the efficiency of that production, specifically, efficiency gains that follow investment in the effort. The effect has large implications for costs[3] and market share, which can increase competitive advantage over time.[4]
- ^ "Solar (photovoltaic) panel prices vs. cumulative capacity". OurWorldInData.org. 2023. Archived from the original on 29 September 2023. OWID credits source data to: Nemet (2009); Farmer & Lafond (2016); International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).
- ^ "Swanson's Law and Making US Solar Scale Like Germany". Greentech Media. 2014-11-24.
- ^ Hirschmann, Winfred B. (1964-01-01). "Profit from the Learning Curve". Harvard Business Review. No. January 1964. ISSN 0017-8012. Retrieved 2020-11-17.
- ^ Henderson, Bruce D. "The Experience Curve – Reviewed II: History, 1973". Retrieved 2013-04-05.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search