Back Soutsuur Afrikaans حمض الهيدروكلوريك Arabic Ácidu clorhídrico AST Xlorid turşusu Azerbaijani هیدروکولوریک اسید AZB Саляная кіслата Byelorussian Хлёравадародная кісьля BE-X-OLD Солна киселина Bulgarian হাইড্রোক্লোরিক অ্যাসিড Bengali/Bangla Hlorovodična kiselina BS

| |||
| |||
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Chlorane[3]
| |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.210.665 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E507 (acidity regulators, ...) | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1789 | ||
| Properties | |||
| HCl(aq) | |||
| Molar mass | 36.46 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless, transparent liquid, fumes in air if concentrated | ||
| Odor | Pungent characteristic | ||
| Density | 1.18 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | Concentration-dependent – see table | ||
| Boiling point | Concentration-dependent – see table | ||
| log P | 0.00[4] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | −5.9 (HCl gas)[5] | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| A09AB03 (WHO) B05XA13 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger[6] | |||
| H290, H314, H335[6] | |||
| P260, P280, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338[6] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
|||
Related compounds
|
Hydrogen chloride | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Hydrochloric acid (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
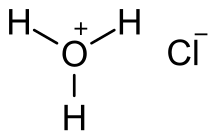
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical.[7][8]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
muriatic_acidwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "spirits of salt". Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- ^ Favre HA, Powell WH, eds. (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 131.
- ^ "Hydrochloric acid". www.chemsrc.com.
- ^ Trummal A, Lipping L, Kaljurand I, Koppel IA, Leito I (May 2016). "Acidity of Strong Acids in Water and Dimethyl Sulfoxide". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 120 (20): 3663–9. Bibcode:2016JPCA..120.3663T. doi:10.1021/acs.jpca.6b02253. PMID 27115918. S2CID 29697201.
- ^ a b c Sigma-Aldrich Co., Hydrochloric acid.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
G&Ewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Ullmannwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search