
Back Olmeke Afrikaans أولمك Arabic Olmeca AST Olmekn BAR Альмекі Byelorussian Олмеки Bulgarian Olmek BJN Olmeked Breton Civilització olmeca Catalan Olmékové Czech
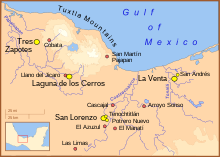 The Olmec heartland, where the Olmec reigned from 1200 to 400 BCE | |
| Geographical range | Veracruz, Mexico |
|---|---|
| Period | Preclassic Era |
| Dates | c. 1200 – 400 BCE |
| Type site | San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán |
| Major sites | La Venta, Tres Zapotes, Laguna de los Cerros |
| Preceded by | Archaic Mesoamerica |
| Followed by | Epi-Olmecs |
The Olmecs (/ˈɒlmɛks, ˈoʊl-/) were the earliest known major Mesoamerican civilization. Following a progressive development in Soconusco, they occupied the tropical lowlands of the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated that the Olmecs derived in part from the neighboring Mokaya or Mixe–Zoque cultures.
The Olmecs flourished during Mesoamerica's formative period, dating roughly from as early as 1200 BCE to about 400 BCE. Pre-Olmec cultures had flourished since about 2500 BCE, but by 1200 BCE, early Olmec culture had emerged, centered on the San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán site near the coast in southeast Veracruz.[1] They were the first Mesoamerican civilization and laid many of the foundations for the civilizations that followed.[2] Among other "firsts", the Olmec appeared to practice ritual bloodletting and played the Mesoamerican ballgame, hallmarks of nearly all subsequent Mesoamerican societies. The aspect of the Olmecs most familiar now is their artwork, particularly the colossal heads.[3] The Olmec civilization was first defined through artifacts which collectors purchased on the pre-Columbian art market in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Olmec artworks are considered among ancient America's most striking.[4]
- ^ Diehl, Richard A. (2004). The Olmecs : America's First Civilization. London: Thames and Hudson. pp. 9–25. ISBN 0-500-28503-9.
- ^ See Pool (2007) p. 2. Although there is wide agreement that the Olmec culture helped lay the foundations for the civilizations that followed, there is disagreement over the extent of the Olmec contributions, and even a proper definition of the Olmec "culture". See "Olmec influences on Mesoamerican cultures" for a deeper treatment of this question.
- ^ See, as one example, Diehl, p. 11.
- ^ See Diehl, p. 108 for the "ancient America" superlatives. The artist and archaeologist Miguel Covarrubias (1957) p. 50 says that Olmec pieces are among the world's masterpieces
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search


