
Back Диаграма на насоченост Bulgarian Diagrama de radiació Catalan Antennendiagramm German Διάγραμμα ακτινοβολίας Greek الگوی تابش Persian Diagramme de rayonnement French עקום קרינה HE Անտենայի ուղղվածության դիագրամ Armenian Diagramma di radiazione Italian Charakterystyka promieniowania anteny Polish
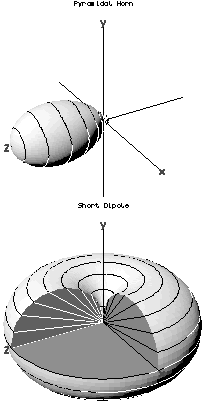
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern (or antenna pattern or far-field pattern) refers to the directional (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.[1][2][3]
Particularly in the fields of fiber optics, lasers, and integrated optics, the term radiation pattern may also be used as a synonym for the near-field pattern or Fresnel pattern.[4] This refers to the positional dependence of the electromagnetic field in the near field, or Fresnel region of the source. The near-field pattern is most commonly defined over a plane placed in front of the source, or over a cylindrical or spherical surface enclosing it.[1][4]
The far-field pattern of an antenna may be determined experimentally at an antenna range, or alternatively, the near-field pattern may be found using a near-field scanner, and the radiation pattern deduced from it by computation.[1] The far-field radiation pattern can also be calculated from the antenna shape by computer programs such as NEC. Other software, like HFSS can also compute the near field.
The far field radiation pattern may be represented graphically as a plot of one of a number of related variables, including; the field strength at a constant (large) radius (an amplitude pattern or field pattern), the power per unit solid angle (power pattern) and the directive gain. Very often, only the relative amplitude is plotted, normalized either to the amplitude on the antenna boresight, or to the total radiated power. The plotted quantity may be shown on a linear scale, or in dB. The plot is typically represented as a three-dimensional graph (as at right), or as separate graphs in the vertical plane and horizontal plane. This is often known as a polar diagram.
- ^ a b c Constantine A. Balanis: “Antenna Theory, Analysis and Design”, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2nd ed. 1982 ISBN 0-471-59268-4
- ^ David K Cheng: “Field and Wave Electromagnetics”, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc., Edition 2, 1998. ISBN 0-201-52820-7
- ^ Edward C. Jordan & Keith G. Balmain; “Electromagnetic Waves and Radiating Systems” (2nd ed. 1968) Prentice-Hall. ISBN 81-203-0054-8
- ^ a b Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, “The IEEE standard dictionary of electrical and electronics terms”; 6th ed. New York, N.Y., Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, c1997. IEEE Std 100-1996. ISBN 1-55937-833-6 [ed. Standards Coordinating Committee 10, Terms and Definitions; Jane Radatz, (chair)]
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search