
Back Maagde-eilande Afrikaans Fæmne Īegland ANG جزر العذراء Arabic Islles Vírxenes AST Vircin adaları Azerbaijani Віргінскія астравы Byelorussian Вирджински острови Bulgarian Inizi Gwerc'h Breton Djevičanska ostrva BS Illes Verges Catalan
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2021) |
 | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Caribbean Sea, Atlantic Ocean |
| Coordinates | 18°12′N 64°48′W / 18.2°N 64.8°W |
| Archipelago | Leeward Islands |
| Insular area | United States Virgin Islands |
| Insular area | Puerto Rico |
| Overseas territory | British Virgin Islands |
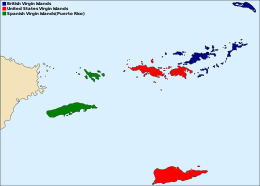
The Virgin Islands (Spanish: Islas Vírgenes) are an archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. They are geologically and biogeographically the easternmost part of the Greater Antilles,[1] While the British Virgin Islands are officially designated as “The Virgin Islands”, the name is most often used to refer to the entire international grouping of the British and United States Virgin Islands together with the Spanish Virgin Islands, which, contrary to their name are in fact officially part of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, itself an unincorporated territory of the United States. Geographically, the northern islands belong to the Puerto Rico Trench. St. Croix is a displaced part of that same geologic structure. Politically, the British Virgin Islands have been governed as the western island group of the Leeward Islands, which are the northern part of the Lesser Antilles, and form the border between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The archipelago is separated from the true Lesser Antilles by the Anegada Passage and from the main island of Puerto Rico by the Virgin Passage.
The islands fall into three different political jurisdictions:
- Virgin Islands, informally referred to as British Virgin Islands, a British overseas territory,
- Virgin Islands of the United States, an unincorporated territory of the United States,
- Spanish Virgin Islands, the easternmost islands of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, itself also an unincorporated territory of the United States.
- ^ Lazell, James (2005). Island: Fact and Theory in Nature. University of California Press. p. 382. ISBN 9780520931596.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search