
Back نيرماترلفير Arabic পিএফ-০৭৩২১৩৩২ Bengali/Bangla Nirmatrelvir Catalan Nirmatrelvir Czech Nirmatrelvir German Νιρματρελβίρη Greek Nirmatrelvir Esperanto Nirmatrelvir French Nirmatrelvir Italian ニルマトレルビル Japanese
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /nɜːrˈmætrəlvɪər/ nur-MAT-rəl-veer or /ˌnɜːrməˈtrɛlvɪər/ NUR-mə-TREL-veer |
| Other names | PF-07321332 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
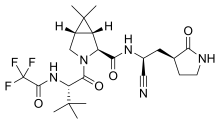
| Formula | C23H32F3N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 499.535 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 192.9 °C (379.2 °F) [3] |
| |
| |

Nirmatrelvir is an antiviral medication developed by Pfizer which acts as an orally active 3C-like protease inhibitor.[3][4][5][6][7] It is part of a nirmatrelvir/ritonavir combination used to treat COVID-19 and sold under the brand name Paxlovid.[8]
Despite earning billions for Pfizer (e.g. $4.1B in Q1 2022 alone[9][10]), research into the efficacy of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir over placebo has shown mixed results (see Research below).
- ^ "Updates to the Prescribing Medicines in Pregnancy database". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 12 May 2022. Archived from the original on 3 April 2022. Retrieved 13 May 2022.
- ^ "Notice: Nirmatrelvir (COVID-19) added to Prescription Drug List (PDL)". Health Canada. 17 January 2022. Archived from the original on 29 May 2022. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Owenwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Şimşek-Yavuz S, Komsuoğlu Çelikyurt FI (August 2021). "Antiviral treatment of COVID-19: An update". Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences. 51 (SI-1): 3372–3390. doi:10.3906/sag-2106-250. PMC 8771049. PMID 34391321. S2CID 237054672.
- ^ Ahmad B, Batool M, Ain QU, Kim MS, Choi S (August 2021). "Exploring the Binding Mechanism of PF-07321332 SARS-CoV-2 Protease Inhibitor through Molecular Dynamics and Binding Free Energy Simulations". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 22 (17): 9124. doi:10.3390/ijms22179124. PMC 8430524. PMID 34502033.
- ^ "Pfizer Announces Additional Phase 2/3 Study Results Confirming Robust Efficacy of Novel COVID-19 Oral Antiviral Treatment Candidate in Reducing Risk of Hospitalization or Death" (Press release). Pfizer. 14 December 2021. Archived from the original on 26 December 2021. Retrieved 25 December 2021 – via Business Wire.
- ^ Vandyck K, Deval J (August 2021). "Considerations for the discovery and development of 3-chymotrypsin-like cysteine protease inhibitors targeting SARS-CoV-2 infection". Current Opinion in Virology. 49: 36–40. doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2021.04.006. PMC 8075814. PMID 34029993.
- ^ "Paxlovid- nirmatrelvir and ritonavir kit". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 31 December 2021. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ "Pfizer pulls Q1 surprise with $4.1B in sales of COVID products, despite plummeting demand". FiercePharma. Retrieved 8 May 2024.
- ^ "Pfizer cuts earnings, revenue guidance as Covid sales slump". CNBC. Retrieved 8 May 2024.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search