In chemistry, a parent structure is the structure of an unadorned ion or molecule from which derivatives can be visualized.[1] Parent structures underpin systematic nomenclature and facilitate classification. Fundamental parent structures have one or no functional groups and often have various types of symmetry. Benzene (C6H6) is a chemical itself consisting of a hexagonal ring of carbon atoms with a hydrogen atom attached to each, and is the parent of many derivatives that have substituent atoms or groups replacing one or more of the hydrogens. Some parents are rare or nonexistent themselves, as in the case of porphine, though many simple and complex derivatives are known.
- Porphyrins
-
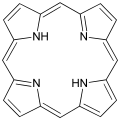
Porphine is the parent of porphyrins.
-
Protoporphyrin IX is a natural derivative of the parent porphine.
-
Octaethylporphyrin is a synthetic derivative of the parent porphine.
- ^ Several examples of parent structures are illustrated in Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search