
Back Eenheidsvektor Afrikaans አሃድ ጨረር Amharic متجه وحدة Arabic Единичен вектор Bulgarian Vector unitari Catalan Jednotkový vektor Czech Пĕрчĕлле вектор CV Enhedsvektor Danish Einheitsvektor German Μοναδιαίο διάνυσμα Greek
In mathematics, a unit vector in a normed vector space is a vector (often a spatial vector) of length 1. A unit vector is often denoted by a lowercase letter with a circumflex, or "hat", as in (pronounced "v-hat").
The term direction vector, commonly denoted as d, is used to describe a unit vector being used to represent spatial direction and relative direction. 2D spatial directions are numerically equivalent to points on the unit circle and spatial directions in 3D are equivalent to a point on the unit sphere.

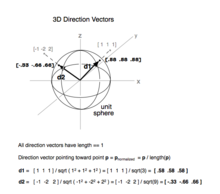
The normalized vector û of a non-zero vector u is the unit vector in the direction of u, i.e.,
where ‖u‖ is the norm (or length) of u.[1][2] The term normalized vector is sometimes used as a synonym for unit vector.
Unit vectors are often chosen to form the basis of a vector space, and every vector in the space may be written as a linear combination form of unit vectors.
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Unit Vector". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2020-08-19.
- ^ "Unit Vectors | Brilliant Math & Science Wiki". brilliant.org. Retrieved 2020-08-19.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search

