
Back جذع الدماغ Arabic بئیین ساپی AZB মস্তিষ্ককাণ্ড Bengali/Bangla ཀླད་གཞུང་ Tibetan Kef empenn Breton Moždano stablo BS Tronc de l'encèfal Catalan لاسکی مێشک CKB Mozkový kmen Czech Hjernestamme Danish
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2013) |
| Brainstem | |
|---|---|
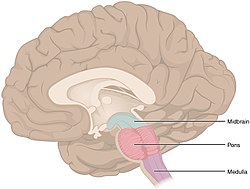 The three distinct parts of the brainstem are colored in this sagittal section of a human brain. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Brain |
| Parts | Medulla, pons, midbrain |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | truncus encephali |
| MeSH | D001933 |
| NeuroNames | 2052, 236 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1565 |
| TA98 | A14.1.03.009 |
| TA2 | 5856 |
| FMA | 79876 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |

The brainstem (or brain stem) is the stalk-like[1]: 152 part of the brain that interconnects the cerebrum and diencephalon with the spinal cord.[2] In the human brain, the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata.[3][1]: 152 The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch.[1]: 152
The brainstem is very small, making up around only 2.6 percent of the brain's total weight.[1]: 195 It has the critical roles of regulating heart and respiratory function, helping to control heart rate and breathing rate.[4] It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem.[5] Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system and the body's sleep cycle.[4] It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the body back to the brain.[4] These pathways include the corticospinal tract (motor function), the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway (fine touch, vibration sensation, and proprioception), and the spinothalamic tract (pain, temperature, itch, and crude touch).[6]
- ^ a b c d Haines, D; Mihailoff, G (2018). Fundamental Neuroscience for Basic and Clinical Applications (5th ed.). ISBN 9780323396325.
- ^ Singh, Vishram (2014). Textbook of Anatomy Head, Neck, and Brain ; Volume III (2nd ed.). p. 363. ISBN 9788131237274.
- ^ Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). p. 474. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ a b c "Brainstem | Definition, Structure, & Function". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2020-05-13.
- ^ "Cranial Nerve Nuclei and Brain Stem Circulation". Neuroanatomy Online. Retrieved 2020-05-13.
- ^ Kolb, B. & Whishaw, I. Q. (2009). Fundamentals of human neuropsychology: Sixth edition. New York, NY: Worth Publishers.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search