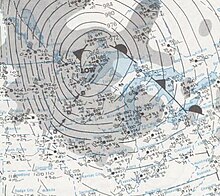
 Surface analysis of the storm on January 11, 1975 | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | January 9, 1975 |
| Exited land | January 12, 1975 |
| Category 3 "Major" winter storm | |
| Regional Snowfall Index: 6.12 (NOAA) | |
| Lowest pressure | 961 mbar (hPa); 28.38 inHg |
| Maximum snowfall or ice accretion | 27 in (69 cm) in Riverton, Minnesota |
| Tornado outbreak | |
| Tornadoes | 45 |
| Maximum rating | F4 tornado |
| Duration | January 9–12, 1975 |
| Highest winds | 81 mph (130 km/h) (highest convective wind) |
| Largest hail | 1+3⁄4 in (4.4 cm) |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 58 (+12 tornadic) |
| Injuries | Unknown (+377 tornadic) |
| Damage | $20,000,000 ($113,250,000 in 2024 USD) (+$43,000,000 tornadic ($243,480,000 in 2024 USD)) |
| Areas affected | Midwestern and Southeastern United States |
Part of the 1974–75 North American winter and tornadoes and tornado outbreaks of 1975 | |
The Great Storm of 1975 (also known as the Super Bowl Blizzard, Minnesota's Storm of the Century, or the Tornado Outbreak of January, 1975) was an intense winter storm system that impacted a large portion of the Central and Southeast United States from January 9–12, 1975. A classic Panhandle hook, the mid-latitude cyclone produced an outbreak of 45 tornadoes in the Southeast U.S. resulting in 12 fatalities, while later dropping over 2 feet (61 cm) of snow and killing 58 people in the Midwest. This storm, which caused blizzard conditions, remains one of the worst blizzards to ever strike parts of the Midwest, as well as one of the largest January tornado outbreaks on record in the United States.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
