
Back فقد الشم Arabic Anosmiya Azerbaijani ঘ্রাণহানি Bengali/Bangla Anosmiezh Breton Anosmija BS Anòsmia Catalan Anosmie Czech Anosmie German Anosmio Esperanto Anosmia Spanish
| Anosmia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Loss of smell, smell blindness,[1] odor blindness |
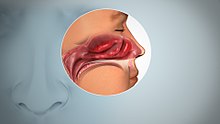 | |
| Inflamed nasal mucosa causing anosmia | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Otorhinolaryngology |
| Types | Partial, total[2] |
Anosmia, also known as smell blindness, is the loss of the ability to detect one or more smells.[1][2] Anosmia may be temporary or permanent.[3] It differs from hyposmia, which is a decreased sensitivity to some or all smells.[2]
Anosmia can be due to a number of factors, including inflammation of the nasal mucosa, blockage of nasal passages, or destruction of temporal lobular tissue.[4] Anosmia stemming from sinus inflammation is due to chronic mucosal changes in the lining of the paranasal sinus and in the middle and superior turbinates.[5][6]
When anosmia is caused by inflammatory changes in the nasal passageways, it is treated simply by reducing inflammation.[7][8] It can be caused by chronic meningitis and neurosyphilis that would increase intracranial pressure over a long period of time,[9] and, in some cases, by ciliopathy,[10] including ciliopathy due to primary ciliary dyskinesia.[11]
The term derives from the Neo-Latin anosmia, based on Ancient Greek ἀν- (an-) + ὀσμή (osmḗ 'smell'; another related term, hyperosmia, refers to an increased ability to smell). Some people may be anosmic for one particular odor, a condition known as "specific anosmia". The absence of the sense of smell from birth is known as congenital anosmia.[12]
In the United States, 3% of people aged over 40 are affected by anosmia.[3]
Anosmia is a common symptom of COVID-19 and can persist as long COVID.[13]
- ^ a b Coon D, Mitterer J (2014). "4. Sensation and perception". Introduction to Psychology: Gateways to Mind and Behavior. Boston: Cengage Learning. p. 136. ISBN 978-1-305-09187-0. LCCN 2014942026.
- ^ a b c Jones N (2010). "2. Making sense of symptoms". In Jones N (ed.). Practical Rhinology. CRC Press. pp. 24–25. ISBN 978-1-4441-0861-3.
- ^ a b Li X, Lui F (6 July 2020). "Anosmia". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29489163. Retrieved 1 December 2020.
- ^ Huynh PP, Ishii LE, Ishii M (July 2020). "What Is Anosmia?". JAMA. 324 (2): 206. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.10966. PMID 32556300. S2CID 219916772.
- ^ Helliwell T (June 2010). "Inflammatory diseases of the nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses". Diagnostic Histopathology. 16 (6): 255–264. doi:10.1016/j.mpdhp.2010.03.008. PMC 7172334. PMID 32336992.
- ^ Lin YT, Yeh TH (2022). "Studies on Clinical Features, Mechanisms, and Management of Olfactory Dysfunction Secondary to Chronic Rhinosinusitis". Frontiers in Allergy. 3: 835151. doi:10.3389/falgy.2022.835151. PMC 8974686. PMID 35386650.
- ^ Knight A (August 1988). "Anosmia". Lancet. 2 (8609): 512. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90160-2. PMID 2900434. S2CID 208793859.(subscription required)
- ^ "Sinusitis Clinical Practice Guideline Quick Reference Tools", Pediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines & Policies, American Academy of Pediatrics, pp. 481–484, 2022-04-11, doi:10.1542/9781610026086-part01-27, ISBN 978-1-61002-608-6, retrieved 2023-11-07
- ^ "Anosmia". The Lancet. 241 (6228): 55. 1943. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)89085-6. S2CID 241387103.
- ^ Uytingco CR, Green WW, Martens JR (2019). "Olfactory Loss and Dysfunction in Ciliopathies: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Therapies". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 26 (17): 3103–3119. doi:10.2174/0929867325666180105102447. PMC 6034980. PMID 29303074.
- ^ Ul Hassan A, Hassan G, Khan SH, Rasool Z, Abida A (January 2009). "Ciliopathy with special emphasis on kartageners syndrome". International Journal of Health Sciences. 3 (1): 65–69. PMC 3068795. PMID 21475513.
- ^ Boesveldt S, Postma EM, Boak D, Welge-Luessen A, Schöpf V, Mainland JD, et al. (September 2017). "Anosmia-A Clinical Review". Chemical Senses. 42 (7): 513–523. doi:10.1093/chemse/bjx025. PMC 5863566. PMID 28531300.
- ^ "Q&A: COVID-19 and loss of smell, taste". Mayo Clinic Health System. Retrieved 2022-02-23.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search