
Back جفاف الساحل Arabic Hungersnot in der Sahelzone German Siccità del Sahel Italian Saheldroogtes Dutch Klęska suszy w Sahelu Polish

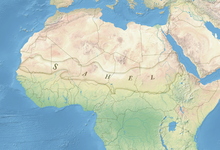
The Sahel region of Africa has long experienced a series of historic droughts, dating back to at least the 17th century. The Sahel region is a climate zone sandwiched between the Sudanian Savanna to the south and the Sahara desert to the north, across West and Central Africa. While the frequency of drought in the region is thought to have increased from the end of the 19th century, three long droughts have had dramatic environmental and societal effects upon the Sahel nations. Famine followed severe droughts in the 1910s, the 1940s, and the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s, although a partial recovery occurred from 1975-80. The most recent drought occurred in 2012.
While at least one particularly severe drought has been confirmed each century since the 17th century, the frequency and severity of recent Sahelian droughts stands out. Famine and dislocation on a massive scale—from 1968 to 1974 and again in the early and mid-1980s—was blamed on two spikes in the severity of the 1960-1980s drought period.[1] From the late 1960s to early 1980s famine killed 100,000 people, left 750,000 dependent on food aid, and affected most of the Sahel's 50 million people.[2] The economies, agriculture, livestock and human populations of much of Mauritania, Mali, Chad, Niger and Burkina Faso (known as Upper Volta during the time of the drought) were severely impacted. As disruptive as the droughts of the late 20th century were, evidence of past droughts recorded in Ghanaian lake sediments suggest that multi-decadal megadroughts were common in West Africa over the past 3,000 years and that several droughts lasted far longer and were far more severe.[3][4]
Since the 1980s, summer rainfall in the Sahel has been increasing; this has been associated with an increase in vegetation, forming what has been called a 'greening' of the Sahel. The observed increase in rainfall is accounted for by enhancements in the African easterly jet, which is known to induce wet anomalies. A 2011 study found that the positional shifts in the African easterly jet and African easterly waves accompanied the northward migration of the Sahel rainband.[5]
- ^ The Sahel region; assessing progress twenty-five years after the great drought. Simon Batterbury, republished paper from 1998 RGS-IBG conference. Global Environmental Change (2001) v11, no 1, 1-95.
- ^ AFRICA ENVIRONMENT OUTLOOK. Past, present and future perspectives Archived 2013-04-16 at archive.today. United Nations Environmental Programme (2002). Retrieved 2009-02-13.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
shanahanwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Severity, Length of Past Megadroughts Dwarf Recent Drought in West Africa. Jackson School of Geosciences Online, April 16, 2009.
- ^ Wang and Gillies (2011)
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search