
Back المجموعة الاقتصادية الأوروآسيوية Arabic Comunidá Económica Eurasiática AST Avrasiya İqtisadi Qrupu Azerbaijani Евразия иҡтисади берләшмәһе Bashkir Еўразійская эканамічная супольнасць Byelorussian Эўразійская эканамічная супольнасьць BE-X-OLD Евразийска икономическа общност Bulgarian Comunitat Econòmica Eurasiàtica Catalan Eurasische Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft German Ευρασιατική Οικονομική Κοινότητα Greek
Eurasian Economic Community Евразийское экономическое сообщество | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
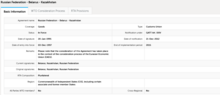
| 2000–2014 | |||||||
| Status | Regional organization | ||||||
| Capital | Moscow (Commission) | ||||||
| Former member states | |||||||
| History | |||||||
• Established | 10 October 2000 | ||||||
| 25 January 2006 | |||||||
| 1 January 2010 | |||||||
| 25 January 2012 | |||||||
• Terminated | 31 December 2014 | ||||||
• EEU established | 1 January 2015 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | Eurasian Economic Union | ||||||
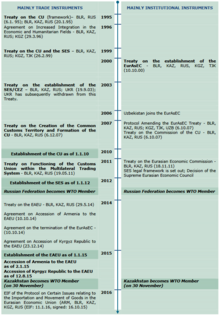

The Eurasian Economic Community (EAEC or EurAsEC) was a regional organisation between 2000 and 2014 which aimed for the economic integration of its member states.[3] The organisation originated from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) on 29 March 1996,[4] with the treaty on the establishment of the Eurasian Economic Community signed on 10 October 2000 in Kazakhstan's capital Astana by Presidents Alexander Lukashenko of Belarus, Nursultan Nazarbayev of Kazakhstan, Askar Akayev of Kyrgyzstan, Vladimir Putin of Russia, and Emomali Rahmon of Tajikistan.[5] Uzbekistan joined the community on 7 October 2005, but later withdrew on 16 October 2008.
During the 14 years, the EAEC implemented a number of economic policies to unify the community. The Customs Union of Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Russia was formed on 1 January 2010, and later renamed the Eurasian Customs Union. The four freedoms of movement modelled after the European Union (goods, capital, services, and people) were fully implemented by 25 January 2012, with the formation of the Eurasian Economic Space.[6][7][8]
On 10 October 2014, an agreement on the termination of the Eurasian Economic Community was signed in Minsk after a session of the Interstate Council of the EAEC. The Eurasian Economic Community was terminated from 1 January 2015 in connection with the launch of the Eurasian Economic Union.[citation needed] While the Eurasian Economic Union effectively replaces the community, membership negotiations with Tajikistan are still ongoing. All other EAEC members have joined the new union.
- ^ "Factual presentation". wto.org. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ a b "WTO | Regional trade agreements". rtais.wto.org. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ Boris N. Mamlyuk (2014). "Regionalizing Multilateralism: The Effect of Russia's Accession to the WTO on Existing Regional Integration Schemes in the Former Soviet Space". UCLA Journal of International Law and Foreign Affairs. 18 (2). SSRN 2412319.
- ^ WTO WT/REG71/1 Archived 2011-12-09 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "WorldTradeLaw.net" (PDF). www.worldtradelaw.net.
- ^ "Могут ли граждане стран, входящих в ЕврАзЭс, свободно перемещаться по территории Сообщества?". www.evrazes.com. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ "Последние новости дня в России и мире сегодня - свежие новости на РБК". РБК. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ Ukraine cannot get observer status at Eurasian Econ Union due to Association Agreement with EU, Russia, Interfax-Ukraine (14 June 2013)
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search