
Back Matriks Afrikaans ማትሪክስ Amharic مصفوفة (رياضيات) Arabic ماتريس ARY Matris Azerbaijani Матрыца (матэматыка) Byelorussian Матрыца BE-X-OLD Матрица (математика) Bulgarian ম্যাট্রিক্স Bengali/Bangla Matrica (matematika) BS
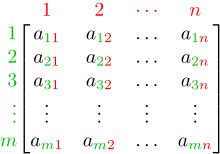
In mathematics, a matrix (pl.: matrices) is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or a property of such an object.
For example,
Matrices are used to represent linear maps and allow explicit computations in linear algebra. Therefore, the study of matrices is a large part of linear algebra, and most properties and operations of abstract linear algebra can be expressed in terms of matrices. For example, matrix multiplication represents the composition of linear maps.
Not all matrices are related to linear algebra. This is, in particular, the case in graph theory, of incidence matrices, and adjacency matrices.[1] This article focuses on matrices related to linear algebra, and, unless otherwise specified, all matrices represent linear maps or may be viewed as such.
Square matrices, matrices with the same number of rows and columns, play a major role in matrix theory. Square matrices of a given dimension form a noncommutative ring, which is one of the most common examples of a noncommutative ring. The determinant of a square matrix is a number associated to the matrix, which is fundamental for the study of a square matrix; for example, a square matrix is invertible if and only if it has a nonzero determinant, and the eigenvalues of a square matrix are the roots of a polynomial determinant.
In geometry, matrices are widely used for specifying and representing geometric transformations (for example rotations) and coordinate changes. In numerical analysis, many computational problems are solved by reducing them to a matrix computation, and this often involves computing with matrices of huge dimension. Matrices are used in most areas of mathematics and most scientific fields, either directly, or through their use in geometry and numerical analysis.
Matrix theory is the branch of mathematics that focuses on the study of matrices. It was initially a sub-branch of linear algebra, but soon grew to include subjects related to graph theory, algebra, combinatorics and statistics.
- ^ However, in the case of adjacency matrices, matrix multiplication or a variant of it allows the simultaneous computation of the number of paths between any two vertices, and of the shortest length of a path between two vertices.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search

