
Back سقف السعر Arabic Maksimum qiymət (iqtisadiyyat) Azerbaijani Höchstpreis German Ανώτατο όριο τιμής Greek Maksimihinta Finnish मूल्य छत Hindi 가격 상한 Korean Cenas griesti Latvian/Lettish Harga bumbung Malay Maximumprijs Dutch

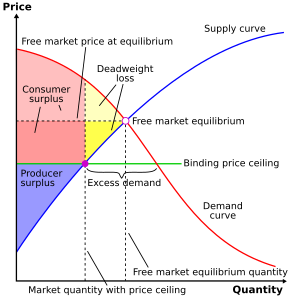
A price ceiling is a government- or group-imposed price control, or limit, on how high a price is charged for a product, commodity, or service. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Such conditions can occur during periods of high inflation, in the event of an investment bubble, or in the event of monopoly ownership of a product, all of which can cause problems if imposed for a long period without controlled rationing, leading to shortages.[1] Further problems can occur if a government sets unrealistic price ceilings, causing business failures, stock crashes, or even economic crises. On the other hand, price ceilings give a government to the power to prevent corporations from price gouging or otherwise setting prices that create negative outcomes for the government's society.
While price ceilings are often imposed by governments, there are also price ceilings that are implemented by non-governmental organizations such as companies, such as the practice of resale price maintenance. With resale price maintenance, a manufacturer and its distributors agree that the distributors will sell the manufacturer's product at certain prices (resale price maintenance), at or below a price ceiling (maximum resale price maintenance) or at or above a price floor.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search