
Back Seznam účastníků Smlouvy o všeobecném zákazu jaderných zkoušek Czech États parties du Traité d'interdiction complète des essais nucléaires French
This article needs to be updated. (October 2023) |
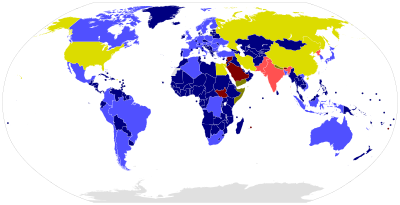
| Annex 2, signed and ratified Annex 2, only signed Annex 2, non-signatory | Not Annex 2, signed and ratified Not Annex 2, only signed Not Annex 2, non-signatory |
The contracting states to the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) are the states that have signed and ratified the international agreement banning all nuclear explosions in all environments. Technically they will not be "parties" until the treaty enters into force,[1] at which point these states will also be Member States of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO), which comes into existence upon entry into force of the treaty. Non-contracting states are also listed, including those that are signatories and those are not. States Signatories are Members of the CTBTO Preparatory Commission.
On September 24, 1996, the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) was opened for signature. All five nuclear weapons states recognized under the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States) signed the treaty, with 66 other states following that day.[2] Fiji became the first state to ratify the treaty on October 10, 1996. As of March 2024, 187 states have signed and 178 states have ratified the treaty. Most recently, Papua New Guinea ratified the treaty in March 2024.[3][4][5][6][7]
Signatures are received at the United Nations Headquarters in New York City by authorized representatives of the state.[8] Ratification is achieved with the approval of either or both chamber of the legislature and executive of the state. The instrument of ratification serves as the document binding the state to the international treaty and can be accepted only with the validating signature of the head of state or other official with full powers to sign it.[9] The instrument is deposited with the Secretary-General of the United Nations.[10]
Under the CTBT, there are 195 Annex 1 states[11] which include a subset of 44 Annex 2 states.[12]
- Annex 1 states are agreed upon by conference and currently comprise all 193 United Nations member states, the Cook Islands, Holy See and Niue. All Annex 1 states may become members of the Executive Council, the principal decision-making body of the organization responsible for supervising its activities.[13] These states are formally bound to the conditions of the treaty; however, their ratification is not necessary for the treaty to come into effect (unless they are also an Annex 2 state).
- Annex 2 states are those that formally participated in the 1996 Conference on Disarmament and possessed nuclear power or research reactors at the time.[14] Annex 2 lists the following 44 States: Algeria, Argentina, Australia, Austria, Bangladesh, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, China, Colombia, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Finland, France, Germany, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Islamic Republic of Iran, Israel, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Netherlands, Norway, Pakistan, Peru, Poland, Republic of Korea, Romania, Russian Federation, Slovakia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, Ukraine, United Kingdom, United States of America, and Vietnam.
Nine Annex 2 states have not ratified the treaty: China, Egypt, Iran, Israel, Russia and the United States have already signed the Treaty, whereas India, North Korea and Pakistan have not signed it. The treaty will come into force only with the signature and ratification of the above Annex 2 states of the treaty, 180 days after they have all deposited their instruments of ratification.[15]
- ^ "Definition of key terms used in the UN Treaty Collection". United Nations. Archived from the original on 1 January 2013. Retrieved 14 January 2013.
- ^ "When did the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty open for signature?". CTBTO Preparatory Commission. Archived from the original on 2010-06-16. Retrieved 2008-07-09.
- ^ "Status of signature and ratification: CTBTO Preparatory Commission". CTBTO Preparatory Commission. 2010-05-26. Retrieved 2010-05-27.
- ^ "Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty". United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs. Retrieved 2013-02-24.
- ^ "Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty". United Nations Treaty Collection. 2013-02-24. Retrieved 2013-02-24.
- ^ Floyd, Robert [@_RobFloyd] (January 26, 2022). "My heartfelt congratulations to Hon. Prime Minister Kausea Natano for his signing of #CTBT instrument of ratification. In doing so, #Tuvalu 🇹🇻 is making a concrete & key contribution to advancing the noble cause of a world free of nuclear testing for now and generations to come. https://t.co/s9C6XqkcFY" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 26 December 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ CTBTO [@CTBTO] (September 22, 2022). "São Tomé and Príncipe ratifies the #CTBT - the 6th ratification during Treaty's 25th anniversary year. Another important milestone on the road to ending #nuclear testing. CTBT is now universal in Central Africa! Another strong stand on nonproliferation and disarmament by Africa. https://t.co/m4wEYTcvYc" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 5 December 2022. Retrieved 26 December 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ "How does a State sign the Treaty?". CTBTO Preparatory Commission. Archived from the original on 2010-06-16. Retrieved 2008-07-09.
- ^ "How does a State ratify the Treaty?". CTBTO Preparatory Commission. Archived from the original on 2010-06-16. Retrieved 2008-07-09.
- ^ "How does a State deposit its instrument of ratification?". CTBTO Preparatory Commission. Archived from the original on 2010-06-16. Retrieved 2008-07-09.
- ^ "Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty". United Nations. Archived from the original on 2014-12-17. Retrieved 2008-07-09. (Article II, Paragraph 28)
- ^ "Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty". United Nations. Archived from the original on 2014-12-17. Retrieved 2008-07-09. (Article XIV)
- ^ "Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty". United Nations. Archived from the original on 2014-12-17. Retrieved 2008-08-02. (Article I, Section C)
- ^ "What are the Annex 2 States?". CTBTO Preparatory Commission. Archived from the original on 2010-06-16. Retrieved 2008-07-09.
- ^ "When will the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty enter into force?". CTBTO Preparatory Commission. Archived from the original on 2010-06-16. Retrieved 2008-07-09.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search