
Back Alabama qraflıqlarının siyahısı Azerbaijani Countys in Alabama BAR Llista de comtats d'Alabama Catalan Rhestr o Siroedd Alabama Welsh Liste der Countys in Alabama German Κατάλογος κομητειών στην Αλαμπάμα Greek Anexo:Condados de Alabama Spanish Alabama maakondade loend Estonian Luettelo Alabaman piirikunnista Finnish Comtés de l'État de l'Alabama French
| Counties of Alabama | |
|---|---|
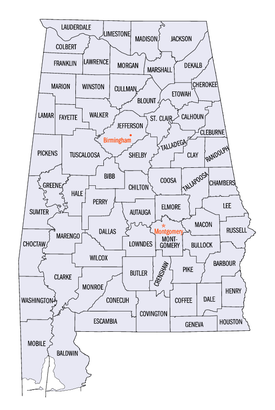 | |
| Location | State of Alabama |
| Number | 67 |
| Populations | Greatest: 662,895 (Jefferson) Least: 7,341 (Greene) Average: 76,246 (2023) |
| Areas | Largest: 1,590 sq mi (4,100 km2) (Baldwin) Smallest: 535 sq mi (1,390 km2) (Etowah) Average: 782 sq mi (2,030 km2) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions |
|
The U.S. state of Alabama has 67 counties.[1] Each county serves as the local level of government within its borders. The land enclosed by the present state borders was joined to the United States of America gradually. Following the American Revolutionary War, West Florida was ceded to Spain by treaty while the remainder was organized primarily as the Mississippi Territory, and later the Alabama Territory.[2] The territorial assembly established some of the earliest county divisions that have survived to the present, including the earliest county formation, that of Washington County, created on June 4, 1800.[3] In 1814, the Treaty of Fort Jackson opened the territory to American settlers, which in turn led to a more rapid rate of county creation. Alabama was admitted to the Union as the 22nd state in 1819.[4] The Alabama state legislature formed additional counties from former native lands as the Indian Removal Act took effect and settlers populated different areas of Alabama.[5] In 1820, Alabama had 29 counties. By 1830 there were 36 and Native Americans still occupied large areas of land in northeast and far western Alabama. By 1840, 49 counties had been created; 52 by 1850; 65 by 1870; and the present 67 counties by 1903.[6] Houston County was the last county created in the state, on February 9, 1903.[3]
According to 2023 U. S. Census data, the average population of Alabama's 67 counties is 76,246, with Jefferson County as the most populous (662,895), and Greene County (7,341) the least.[7] The average land area is 756 sq mi (1,958 km2). The largest county is Baldwin (1,590 sq mi, 4,118 km2) and the smallest is Etowah (535 sq mi, 1,386 km2).[8] The Constitution of Alabama requires that any new county in Alabama cover at least 600 square miles (1,600 km2) in area, effectively limiting the creation of new counties in the state.[9]
The Alabama Department of Revenue's Motor Vehicle Division issues standard automobile license plates that bear a one- or two-digit number identifying the county in which the vehicle is registered. This number is given in the fourth column in the table below. The first three prefixes are reserved for the state's historically most populous counties, and thereafter proceed alphabetically. Individual license plate numbers are assigned sequentially in each licensing office. The numbers are in the format XAA1111 or XXAA111, depending on whether the prefix is one or two digits. Overflow registrations are accommodated by substituting a letter for one of the registration numbers, such that XXZ999Z is followed by XXA0A0A.[10]
The Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) code, used by the United States government to uniquely identify counties, is provided with each entry. The FIPS code links in the table point to U. S. Census "quick facts" pages for each county. Alabama's FIPS state code is 01.
- ^ "List of Alabama Counties". Bama Politics. October 23, 2018. Retrieved August 4, 2020.
- ^ "Alabama History Timeline, 1701–1800". Alabama Department of Archives and History. Retrieved May 18, 2009.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
NACOwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Alabama History Timeline, 1801–1860". Alabama Department of Archives and History. Retrieved May 18, 2009.
- ^ "Alabama Counties: Cherokee". Alabama Department of Archives and History. Retrieved December 29, 2008.
- ^ Foscue, Virginia O. (1989) Place Names in Alabama. Tuscaloosa, Alabama: University of Alabama Press. ISBN 0-8173-0410-X
- ^ "U.S. Census website". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved March 20, 2024.
- ^ "2010 Census U.S. Gazetteer Files". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved March 13, 2011.
- ^ Wikisource:Alabama State Constitution of 1901/Initial Constitution#Section 39
- ^ Nicholson, David. "Alabama License Plates, 1969–present". License Plates of North America, 1969–present. Retrieved August 8, 2007.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search