
Back Distikstoftrioksied Afrikaans ثلاثي أكسيد ثنائي النتروجين Arabic دینیتروژن تریاوکسید AZB Triòxid de dinitrogen Catalan Oxid dusitý Czech Dinitrogentrioxid Danish Distickstofftrioxid German Dinitrogena trioksido Esperanto Óxido de nitrógeno(III) Spanish دینیتروژن تریاکسید Persian
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-Oxonitramide[1]
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.013 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2421 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 76.011 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Deep blue liquid |
| Density |
|
| Melting point | −100.7[2] °C (−149.3 °F; 172.5 K) |
| Boiling point | 3.5 °C (38.3 °F; 276.6 K) (dissociates[2]) |
| reacts to form nitrous acid | |
| Solubility | soluble in ether |
| −16.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
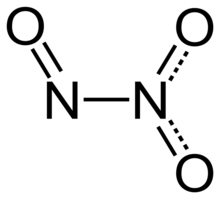
| Structure | |
| planar, Cs | |
| 2.122 D | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
65.3 J/(mol·K) |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
314.63 J/(mol·K) |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
91.20 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[3] | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H270, H280, H310, H310+H330, H314, H330 | |
| P220, P244, P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+P330+P331, P302+P350, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P320, P321, P322, P361, P363, P370+P376, P403, P403+P233, P405, P410+P403, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dinitrogen trioxide (also known as nitrous anhydride) is the inorganic compound with the formula N2O3. It is a nitrogen oxide. It forms upon mixing equal parts of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide and cooling the mixture below −21 °C (−6 °F):[4]
- •
NO + •
NO
2 ⇌ N
2O
3
Dinitrogen trioxide is only isolable at low temperatures, i.e. in the liquid and solid phases. In liquid and solid states, it has a deep blue color.[2] At higher temperatures the equilibrium favors the constituent gases, with KD = 193 kPa (25 °C).[5][clarification needed]
This compound is sometimes called "nitrogen trioxide", but this name properly refers to another compound, the (uncharged) nitrate radical •NO3.
- ^ "Dinitrogen trioxide".
- ^ a b c Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 444. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ "Dinitrogen trioxide". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1984). Chemistry of the Elements. Oxford: Pergamon Press. pp. 521–22. ISBN 978-0-08-022057-4.
- ^ Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
