
Back Makedonisch-Römische Kriege ALS الحروب المقدونية Arabic Guerres macedonies AST Makedoniya müharibələri Azerbaijani Македонски войни Bulgarian মেসিডনীয় যুদ্ধসমূহ Bengali/Bangla Guerres macedòniques Catalan Makedonské války Czech Makedonisch-Römische Kriege German Μακεδονικοί Πόλεμοι Greek
|
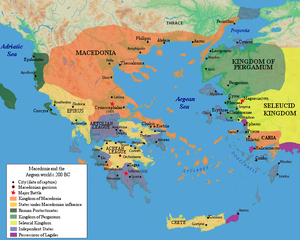 |
The Macedonian Wars (214–148 BC) were a series of conflicts fought by the Roman Republic and its Greek allies in the eastern Mediterranean against several different major Greek kingdoms. They resulted in Roman control or influence over Greece and the rest of the eastern Mediterranean basin, in addition to their hegemony in the western Mediterranean after the Punic Wars. Traditionally, the "Macedonian Wars" include the four wars with Macedonia, in addition to one war with the Seleucid Empire, and a final minor war with the Achaean League (which is often considered to be the final stage of the final Macedonian War). The most significant war was fought with the Seleucid Empire, while the war with Macedonia was the second, and both of these wars effectively marked the end of these empires as major world powers, even though neither of them led immediately to overt Roman domination.[1] Four separate wars were fought against the weaker power, Macedonia, due to its geographic proximity to Rome, though the last two of these wars were against haphazard insurrections rather than powerful armies.[2] Roman influence gradually dissolved Macedonian independence and digested it into what was becoming a leading empire. The outcome of the war with the now-deteriorating Seleucid Empire was ultimately fatal to it as well, though the growing influence of Parthia and Pontus prevented any additional conflicts between it and Rome.[2]
From the close of the Macedonian Wars until the early Roman Empire, the eastern Mediterranean remained an ever shifting network of polities with varying levels of independence from, dependence on, or outright military control by, Rome.[3] According to Polybius,[4] who sought to trace how Rome came to dominate the Greek east in less than a century, Rome's wars with Greece were set in motion after several Greek city-states sought Roman protection against the Macedonian Kingdom and Seleucid Empire in the face of a destabilizing situation created by the weakening of Ptolemaic Egypt.[5]
In contrast to the west, the Greek east had been dominated by major empires for centuries, and Roman influence and alliance-seeking led to wars with these empires that further weakened them and therefore created an unstable power vacuum that only Rome was capable of pacifying.[6] This had some important similarities (and some important differences) to what had occurred in Italy centuries earlier, but was this time on a continental scale. Historians[7][failed verification] see the growing Roman influence over the east, as with the west, not as a matter of intentional empire-building, but constant crisis management narrowly focused on accomplishing short-term goals within a highly unstable, unpredictable, and inter-dependent network of alliances and dependencies.[8] With some major exceptions of outright military rule (such as parts of mainland Greece), the eastern Mediterranean world remained an alliance of independent city-states and kingdoms (with varying degrees of independence, both de jure and de facto) until it transitioned into the Roman Empire.[9] It wasn't until the time of the Roman Empire that the eastern Mediterranean, along with the entire Roman world, was organized into provinces under explicit Roman control.[10]
- ^ Eckstein 2008, p. 61.
- ^ a b Eckstein 2008, p. 62.
- ^ Eckstein 2008, p. 78.
- ^ Eckstein 2008, p. 12.
- ^ Eckstein 2008, p. 40.
- ^ Eckstein 2008, p. 45.
- ^ Goldsworthy 2003, p. 36.
- ^ Eckstein 2008, p. 38.
- ^ Madden 2008, p. 62.
- ^ Madden 2008, p. 64.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search