This article appears to be a dictionary definition. (October 2023) |
Active shooter is a term used to describe the perpetrator of an ongoing mass shooting. The term is primarily used to characterize shooters who are targeting victims indiscriminately and at a large scale, who oftentimes, will either commit suicide or intend to be killed by police. More generally, an active perpetrator of a mass murder may be referred to as an active killer.
The Federal Bureau of Investigation defines an active shooter as "one or more individuals actively engaged in killing or attempting to kill people in a populated area", excluding gun-related incidents that were the result of self-defense, gang or drug violence, residential or domestic disputes, crossfire as a byproduct of another ongoing criminal act, controlled barricade or hostage situations, or actions that appeared not to have put other people in peril.[2] In 2008, the United States Department of Homeland Security defined an active shooter as "an individual actively engaged in killing or attempting to kill people in a confined and populated area; in most cases, active shooters use firearms and there is no pattern or method to their selection of victims."[3]
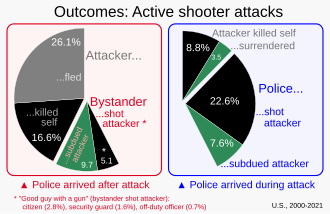
Most incidents occur at locations in which the killers find little impediment in pressing their attack. Locations are generally described as soft targets, that is, they carry limited security measures to protect members of the public. In most instances, shooters die by suicide, are shot by police, or surrender when confrontation with responding law enforcement becomes unavoidable, and active shooter events are often over in 10 to 15 minutes.[3] "According to New York City Police Department (NYPD) statistics, 46 percent of active shooter incidents are ended by the application of force by police or security, 40 percent end in the shooter's suicide, 14 percent of the time the shooter surrenders, and in less than 1 percent of cases the violence ends with the attacker fleeing."[4]
- ^ Buchanan, Larry; Leatherby, Lauren (June 22, 2022). "Who Stops a 'Bad Guy With a Gun'?". The New York Times. Archived from the original on June 22, 2022.
Data source: Advanced Law Enforcement Rapid Response Training Center
- ^ Active Shooter Incidents in the United States in 2021 (Report). Washington, D.C.: Federal Bureau of Investigation/U.S. Department of Justice/Advanced Law Enforcement Rapid Response Training at Texas State University. 2022. Retrieved January 8, 2023.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
dhswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "The Active Shooter Threat" (PDF). MSA Special Analysis.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
