Back Yukon Afrikaans ዩካን Amharic Geocon ANG يوكون (إقليم) Arabic ܝܘܩܘܢ ARC Yukón AST Yukon Azerbaijani یوکان AZB Yukon BAN Yukon (Territorium) BAR
Yukon | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates: 63°N 135°W / 63°N 135°W[1] | |
| Country | Canada |
| Before confederation | District of Yukon |
| Confederation | June 13, 1898 (9th) |
| Capital (and largest city) | Whitehorse |
| Largest metro | Whitehorse |
| Government | |
| • Type | Parliamentary system |
| • Commissioner | Adeline Webber |
| • Premier | Ranj Pillai |
| Legislature | Yukon Legislative Assembly |
| Federal representation | Parliament of Canada |
| House seats | 1 of 338 (0.3%) |
| Senate seats | 1 of 105 (1%) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 482,443 km2 (186,272 sq mi) |
| • Land | 474,391 km2 (183,163 sq mi) |
| • Water | 8,052 km2 (3,109 sq mi) 1.7% |
| • Rank | 9th |
| 4.8% of Canada | |
| Population (2021) | |
| • Total | 40,232[2] |
| • Estimate (Q1 2024) | 45,387[3] |
| • Rank | 12th |
| • Density | 0.08/km2 (0.2/sq mi) |
| Demonyms | Yukoner FR: Yukonnais(e) |
| Official languages | |
| GDP | |
| • Rank | 13th |
| • Total (2017) | C$3.089 billion[5] |
| • Per capita | C$75,141 (3rd) |
| HDI | |
| • HDI (2021) | 0.930[6] — Very high (4th) |
| Time zone | UTC−07:00 |
| Canadian postal abbr. | YT |
| Postal code prefix | |
| ISO 3166 code | CA-YT |
| Flower | Fireweed |
| Tree | Subalpine fir[7] |
| Bird | Common raven |
| Rankings include all provinces and territories | |
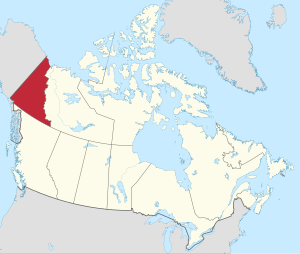
Yukon (formerly called the Yukon Territory and referred to as the Yukon)[8] is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It is the third-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 45,148 as of 2023. However, Whitehorse, the territorial capital, is the largest settlement in any of the three territories.[9]
Yukon was split from the Northwest Territories in 1898 as the Yukon Territory. The federal government's Yukon Act, which received royal assent on March 27, 2002, established "Yukon" as the territory's official name, although Yukon Territory remains in popular usage. Canada Post uses the territory's internationally approved postal abbreviation of YT.[10][8] In 2021, territorial government policy was changed so that "The Yukon" would be recommended for use in official territorial government materials.[11]
Although officially bilingual (English and French), the Yukon government recognizes First Nations languages.
At 5,959 m (19,551 ft), Yukon's Mount Logan, in Kluane National Park and Reserve, is the highest mountain in Canada and the second-highest on the North American continent (after Denali in the U.S. state of Alaska). Most of the Yukon has a subarctic climate, characterized by long, cold winters and brief, warm summers. The coastal area along the Arctic Ocean has a tundra climate.
Notable rivers include the Yukon, Pelly, Stewart, Peel, White, Liard, and Tatshenshini.
- ^ "Yukon". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada.
- ^ "Population and dwelling counts, for Canada, provinces and territories, 2016 and 2011 censuses". Statistics Canada. February 9, 2022. Retrieved February 10, 2022.
- ^ "Population estimates, quarterly". Statistics Canada. September 27, 2023. Archived from the original on September 28, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2023.
- ^ "The Legal Context of Canada's Official Languages". University of Ottawa. Archived from the original on December 21, 2016. Retrieved October 7, 2016.
- ^ "Gross domestic product, expenditure-based, by province and territory (2017)". Statistics Canada. September 22, 2019. Retrieved September 22, 2019.
- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Subnational HDI - Global Data Lab". globaldatalab.org. Retrieved May 18, 2022.
- ^ "Government of Yukon: Emblems and Symbols". Archived from the original on February 12, 2012.
- ^ a b "Yukon Act, SC 2002, c 7". CanLII. Retrieved February 22, 2011.
- ^ Canada, Government of Canada, Statistics (February 8, 2017). "Population and Dwelling Count Highlight Tables, 2016 Census". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved February 8, 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Table 8 Abbreviations and codes for provinces and territories, 2011 Census". Statistics Canada. December 30, 2015. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ "Back to 'the' Yukon: The big return of a 3-letter word". CBC. August 10, 2021. Retrieved November 3, 2021.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search