
Back انتخابات الرئاسة الأمريكية 1852 Arabic Præsidentvalget i USA 1852 Danish Präsidentschaftswahl in den Vereinigten Staaten 1852 German Elecciones presidenciales de Estados Unidos de 1852 Spanish Yhdysvaltain presidentinvaalit 1852 Finnish Élection présidentielle américaine de 1852 French הבחירות לנשיאות ארצות הברית 1852 HE Elezioni presidenziali negli Stati Uniti d'America del 1852 Italian 1852年アメリカ合衆国大統領選挙 Japanese 1852년 미국 대통령 선거 Korean
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
296 members of the Electoral College 149 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 69.5%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
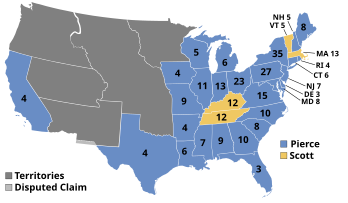 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Pierce/King and Yellow by Scott/Graham. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes cast by each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1852 United States presidential election was the 17th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 1852. Democrat Franklin Pierce defeated Whig nominee General Winfield Scott. A third party candidate from the Free Soil party, John P. Hale, also ran and came in third place, but got no electoral votes.
Incumbent Whig President Millard Fillmore had succeeded to the presidency in 1850 upon the death of President Zachary Taylor. Fillmore endorsed the Compromise of 1850 and enforced the Fugitive Slave Law. This earned Fillmore Southern voter support and Northern voter opposition. On the 53rd ballot of the sectionally divided 1852 Whig National Convention, Scott defeated Fillmore for the nomination. Democrats divided among four major candidates at the 1852 Democratic National Convention. On the 49th ballot, dark horse candidate Franklin Pierce won nomination by consensus compromise. The Free Soil Party, a third party opposed to the extension of slavery in the United States and into the territories, nominated New Hampshire Senator John P. Hale.
With few policy differences between the two major candidates, the election became a personality contest. Though Scott had commanded in the Mexican–American War, Pierce also served. Scott strained Whig Party unity as his anti-slavery reputation gravely damaged his campaign in the South. A group of Southern Whigs and a separate group of Southern Democrats each nominated insurgent tickets, but both efforts failed to attract support.
Pierce and running mate William R. King won a comfortable popular majority, carrying 27 of the 31 states. Pierce won the highest share of the electoral vote since James Monroe's uncontested 1820 re-election. The Free Soil Party regressed to less than five percent of the national popular vote, down from more than ten percent in 1848, while overwhelming defeat and disagreement about slavery soon drove the Whig Party to disintegrate. Anti-slavery Whigs and Free Soilers would ultimately coalesce into the new Republican Party, which would quickly become a formidable movement in the free states.
Not until 1876 would Democrats again win a majority of the popular vote for president, and not until 1932 would they win a majority in both the popular vote and the electoral college.
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search

