
Back خريطة الطقس Arabic Sinoptik xəritə Azerbaijani Mapa meteorològic Catalan ᏙᏱ ᏂᎦᎵᏍᏔᏂᏙᎲ ᎧᏃᎮᏍᎩ CHR نەخشەی کەشوھەوا CKB Meteorologická mapa Czech Wetterkarte German Μετεωρολογικός χάρτης Greek Mapa meteorológico Spanish Ilmakaart Estonian
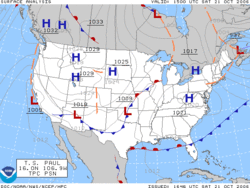
A weather map, also known as synoptic weather chart, displays various meteorological features across a particular area at a particular point in time and has various symbols which all have specific meanings.[1] Such maps have been in use since the mid-19th century and are used for research and weather forecasting purposes. Maps using isotherms show temperature gradients,[2] which can help locate weather fronts. Isotach maps, analyzing lines of equal wind speed,[3] on a constant pressure surface of 300 or 250 hPa show where the jet stream is located. Use of constant pressure charts at the 700 and 500 hPa level can indicate tropical cyclone motion. Two-dimensional streamlines based on wind speeds at various levels show areas of convergence and divergence in the wind field, which are helpful in determining the location of features within the wind pattern. A popular type of surface weather map is the surface weather analysis, which plots isobars to depict areas of high pressure and low pressure. Cloud codes are translated into symbols and plotted on these maps along with other meteorological data that are included in synoptic reports sent by professionally trained observers.
- ^ Encarta (2009). "Chart". Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on 2007-11-01. Retrieved 2007-11-25.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
DataAirwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Jay Snively (2010). "H-I-J". MAPS GPS. Archived from the original on 2018-04-02. Retrieved 2010-01-30.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search