
Back Kubus Afrikaans Cubo AN مكعب Arabic مكعب ARY Hexaedru AST Kub Azerbaijani کۆب AZB Куб Bashkir Куб Byelorussian Куб Bulgarian
| Regular hexahedron | |
|---|---|
 (Click here for rotating model) | |
| Type | Platonic solid |
| Elements | F = 6, E = 12 V = 8 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 6{4} |
| Conway notation | C |
| Schläfli symbols | {4,3} |
| t{2,4} or {4}×{} tr{2,2} {}×{}×{} = {}3 | |
| Face configuration | V3.3.3.3 |
| Wythoff symbol | 3 | 2 4 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry | Oh, B3, [4,3], (*432) |
| Rotation group | O, [4,3]+, (432) |
| References | U06, C18, W3 |
| Properties | regular, convexzonohedron, Hanner polytope |
| Dihedral angle | 90° |
 4.4.4 (Vertex figure) |
 Octahedron (dual polyhedron) |
 Net | |

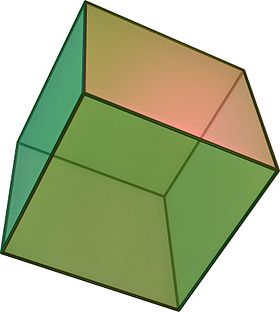
In geometry, a cube[a] is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets, or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner, it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.[1]
The cube is the only regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices.
The cube is also a square parallelepiped, an equilateral cuboid, a right rhombohedron, and a 3-zonohedron. It is a regular square prism in three orientations, and a trigonal trapezohedron in four orientations.
The cube is dual to the octahedron. It has cubical or octahedral symmetry, and is the only convex polyhedron whose faces are all squares. Its generalization for higher-dimensional spaces is called a hypercube.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search