
Back Murrayrivier Afrikaans Murray River ALS نهر موراي Arabic نهر موراى ARZ Ríu Murray AST Murrey çayı Azerbaijani مورای چایی AZB Муррей (йылға) Bashkir Мурэй Byelorussian Марэй (рака) BE-X-OLD
| Murray River (Millewa / Dhungala (Tongala)) | |
|---|---|
 The course of the Murray River (click to enlarge) | |
| Location | |
| Country | Australia |
| State | New South Wales, South Australia and Victoria |
| Cities | Albury, Wodonga, Echuca, Swan Hill, Mildura, Renmark, Murray Bridge |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Cowombat Flat |
| • location | Australian Alps, NSW |
| • coordinates | 36°47′46″S 148°11′40″E / 36.79611°S 148.19444°E |
| • elevation | 1,430 m (4,690 ft) |
| Mouth | Murray Mouth |
• location | near Goolwa South |
• coordinates | 35°33′32″S 138°52′48″E / 35.55889°S 138.88000°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 2,508 km (1,558 mi) |
| Basin size | 1,061,469 km2 (409,835 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 767 m3/s (27,100 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Mitta Mitta River, Kiewa River, Ovens River, Goulburn River, Campaspe River, Loddon River |
| • right | Swampy Plain River, Murrumbidgee River, Darling River |
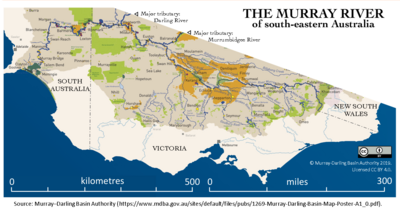
The Murray River (in South Australia: River Murray)[note 1] (Ngarrindjeri: Millewa, Yorta Yorta: Dhungala[2] (Tongala))[3] is a river in Southeastern Australia. It is Australia's longest river at 2,508 km (1,558 mi) extent.[4] Its tributaries include five of the next six longest rivers of Australia (the Murrumbidgee, Darling, Lachlan, Warrego and Paroo Rivers). Together with that of the Murray, the catchments of these rivers form the Murray–Darling basin, which covers about one-seventh the area of Australia. It is widely considered Australia's most important irrigated region.
The Murray rises in the Australian Alps, draining the western side of Australia's highest mountains, then meanders northwest across Australia's inland plains, forming the border between the states of New South Wales and Victoria as it flows into South Australia. From an east–west direction it turns south at Morgan for its final 315 km (196 mi), reaching the eastern edge of Lake Alexandrina, which fluctuates in salinity. The water then flows through several channels around Hindmarsh Island and Mundoo Island. There it is joined by lagoon water from The Coorong to the south-east before emptying into the Great Australian Bight (often referenced on Australian maps as the Southern Ocean) through the Murray Mouth, 10 km (6.2 mi) east of Goolwa South.[5] Despite discharging considerable volumes of water at times, particularly before the advent of large-scale river regulation, the waters at the Murray Mouth are almost invariably slow and shallow.
As of 2010[update], the Murray River system received 58 per cent of its natural flow; the figure varies considerably.[6]
The border between Victoria and New South Wales (NSW) lies along the top of the southern or left bank of the Murray River.[7]
- ^ "Geographical names guidelines". Planning and property. Attorney-General's Department (Government of South Australia). August 2020. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
- ^ "History - Yorta Yorta Traditional Owner Land Management Board". www.yytolmb.com.au. YYTOLMB. Retrieved 19 January 2023.
- ^ "People of the Murray River - Aboriginal communities". www.murrayriver.com.au.
- ^ "(Australia's) Longest Rivers". Geoscience Australia. 10 December 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
MDBC mouthwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Guide to the proposed Basin Plan, Murray Darling Basin Authority 2010 Archived 13 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Guidelines for the Determination of the State Border Between New South Wales and Victoria Along the Murray River" (PDF).
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search