
Back فوسفونات Arabic Fosfonat BS Fosfonat Catalan Fosfonáty Czech Phosphonate German Fosfonato Spanish Fosfonato Basque فسفونات Persian Fosfonaatit Finnish Acide phosphonique French

In organic chemistry, phosphonates or phosphonic acids are organophosphorus compounds containing C−PO(OR)2 groups (where R = alkyl, aryl, or just hydrogen). Phosphonic acids, typically handled as salts, are generally nonvolatile solids that are poorly soluble in organic solvents, but soluble in water and common alcohols.
Many commercially important compounds are phosphonates, including glyphosate (the active molecule of the herbicide Roundup), and ethephon, a widely used plant growth regulator. Bisphosphonates are popular drugs for treatment of osteoporosis.[1]
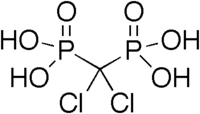
In biochemistry and medicinal chemistry, phosphonate groups are used as stable bioisosteres for phosphate, such as in the antiviral nucleotide analog, Tenofovir, one of the cornerstones of anti-HIV therapy. And there is an indication that phosphonate derivatives are "promising ligands for nuclear medicine."[2]
- ^ Svara, J.; Weferling, N.; Hofmann, T. "Phosphorus Compounds, Organic," in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2008. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_545.pub2.
- ^ Pazderová, Lucia; David, Tomáš; Hlinová, Veronika; Plutnar, Jan; Kotek, Jan; Lubal, Přemysl; Kubíček, Vojtěch; Hermann, Petr (2020-06-15). "Cross-Bridged Cyclam with Phosphonate and Phosphinate Pendant Arms: Chelators for Copper Radioisotopes with Fast Complexation". Inorganic Chemistry. 59 (12): 8432–8443. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c00856. ISSN 0020-1669. PMID 32437603. S2CID 218834212.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search