
Back فينيثيلامينات Arabic Phenylethylamine German Fenetilamina sustituida Spanish Phényléthylamine French Βeta-Phenylalkylaminnen LB Pochodne fenyloetyloaminy Polish Supstituisani fenetilamin Serbo-Croatian Supstituisani fenetilamin Serbian 苯乙胺衍生物 Chinese
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2014) |
| Substituted phenethylamine | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
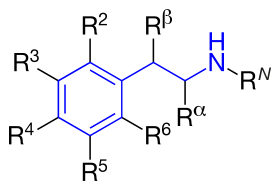 The structural formula of phenethylamine with marked substitution points. Phenethylamine is obtained when R2=R3=R4=R5=R6=RN=Rα=Rβ=H. | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Chemical class | Substituted derivatives of phenethylamine |
| Legal status | |
| In Wikidata | |
Substituted phenethylamines (or simply phenethylamines) are a chemical class of organic compounds that are based upon the phenethylamine structure;[note 1] the class is composed of all the derivative compounds of phenethylamine which can be formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the phenethylamine core structure with substituents.
The structural formula of any substituted phenethylamine contains a phenyl ring that is joined to an amino (NH) group via a two-carbon sidechain. Hence, any substituted phenethylamine can be classified according to the substitution of hydrogen (H) atoms on phenethylamine's phenyl ring, sidechain, or amino group with a specific group of atoms.
Many substituted phenethylamines are psychoactive drugs which belong to a variety of different drug classes, including central nervous system stimulants (e.g., amphetamine), hallucinogens (e.g., 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine a.k.a. mescaline), 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine a.k.a. DOM), entactogen (e.g. MDA), appetite suppressants (e.g. phentermine), nasal decongestants and bronchodilators (e.g., levomethamphetamine and pseudoephedrine), antidepressants (e.g. bupropion and phenelzine), antiparkinson agents (e.g., selegiline), and vasopressors (e.g., ephedrine), among others.[1][2] Many of these psychoactive compounds exert their pharmacological effects primarily by modulating monoamine neurotransmitter systems; however, there is no mechanism of action or biological target that is common to all members of this subclass.[medical citation needed]
Numerous endogenous compounds – including hormones, catecholamines such as dopamine and noradrenaline, and many trace amines (e.g. adrenaline, phenethylamine itself, tyramine, thyronamine, and iodothyronamine) – are substituted phenethylamines. Several notable recreational drugs, such as MDMA (ecstasy), methamphetamine, and cathinone, are also members of the class. All of the substituted amphetamines and substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamines are substituted phenethylamines as well.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Inan, Funda; Brunt, Tibor M.; Contrucci, Ramon R.; Hondebrink, Laura; Franssen, Eric J. F. (2020). "Novel Phenethylamines and Their Potential Interactions With Prescription Drugs: A Systematic Critical Review". Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. 42 (2): 271–281. doi:10.1097/ftd.0000000000000725. ISSN 0163-4356. PMID 32022784. S2CID 211035606.
- ^ Wills, Brandon; Erickson, Timothy (2 February 2012). "Psychoactive Phenethylamine, Piperazine, and Pyrrolidinophenone Derivatives". Medical Toxicology of Drug Abuse: 156–192. doi:10.1002/9781118105955.ch10. ISBN 978-0-471-72760-6.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search